Synthetic hormone-responsive transcription factors can monitor and re-program plant development
- PMID: 29714687
- PMCID: PMC5976440
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.34702
Synthetic hormone-responsive transcription factors can monitor and re-program plant development
Abstract
Developmental programs sculpt plant morphology to meet environmental challenges, and these same programs have been manipulated to increase agricultural productivity (Doebley et al., 1997; Khush, 2001). Hormones coordinate these programs, creating chemical circuitry (Vanstraelen and Benková, 2012) that has been represented in mathematical models (Refahi et al., 2016; Prusinkiewicz et al., 2009); however, model-guided engineering of plant morphology has been limited by a lack of tools (Parry et al., 2009; Voytas and Gao, 2014). Here, we introduce a novel set of synthetic and modular
Keywords: A. thaliana; CRISPR Cas9; auxin; engineered development; phyllotaxy; phytohormone; plant biology; synthetic transcription factor.
© 2018, Khakhar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AK, AL, AL, EK, JN No competing interests declared
Figures


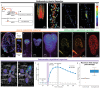
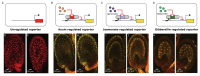

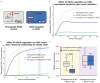
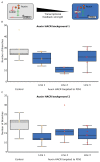
References
-
- Band LR, Wells DM, Fozard JA, Ghetiu T, French AP, Pound MP, Wilson MH, Yu L, Li W, Hijazi HI, Oh J, Pearce SP, Perez-Amador MA, Yun J, Kramer E, Alonso JM, Godin C, Vernoux T, Hodgman TC, Pridmore TP, Swarup R, King JR, Bennett MJ. Systems analysis of auxin transport in the Arabidopsis root apex. The Plant Cell. 2014;26:862–875. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.119495. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burks T, Villegas F, Hannan M, Flood S, Sivaraman B, Subramanian V, Sikes J. Engineering and horticultural aspects of robotic fruit harvesting: opportunities and constraints. HortTechnology. 2005;15:79–87.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

