Divergent effects of strontium and calcium-sensing receptor positive allosteric modulators (calcimimetics) on human osteoclast activity
- PMID: 29714810
- PMCID: PMC6177624
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14344
Divergent effects of strontium and calcium-sensing receptor positive allosteric modulators (calcimimetics) on human osteoclast activity
Abstract
Background and purpose: Strontium ranelate, a drug approved and until recently used for the treatment of osteoporosis, mediates its effects on bone at least in part via the calcium-sensing (CaS) receptor. However, it is not known whether bone-targeted CaS receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs; calcimimetics) represent an alternative (or adjunctive) therapy to strontium (Sr2+ o ).
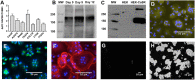
Experimental approach: We assessed three structurally distinct calcimimetics [cinacalcet, AC-265347 and a benzothiazole tri-substituted urea (BTU-compound 13)], alone and in combination with extracellular calcium (Ca2+ o ) or Sr2+ o , in G protein-dependent signalling assays and trafficking experiments in HEK293 cells and their effects on cell differentiation, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) activity and hydroxyapatite resorption assays in human blood-derived osteoclasts.
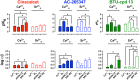
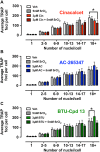
Key results: Sr2+ o activated CaS receptor-dependent signalling in HEK293 cells in a similar manner to Ca2+ o , and inhibited the maturation, TRAP expression and hydroxyapatite resorption capacity of human osteoclasts. Calcimimetics potentiated Ca2+ o - and Sr2+ o -mediated CaS receptor signalling in HEK293 cells with distinct biased profiles, and only cinacalcet chaperoned an endoplasmic reticulum-retained CaS mutant receptor to the cell surface in HEK293 cells, indicative of a conformational state different from that engendered by AC-265347 and BTU-compound 13. Intriguingly, only cinacalcet modulated human osteoclast function, reducing TRAP activity and profoundly inhibiting resorption.
Conclusion and implications: Although AC-265347 and BTU-compound 13 potentiated Ca2+ o - and Sr2+ o -induced CaS receptor activation, they neither replicated nor potentiated the ability of Sr2+ o to inhibit human osteoclast function. In contrast, the FDA-approved calcimimetic, cinacalcet, inhibited osteoclast TRAP activity and hydroxyapatite resorption, which may contribute to its clinical effects on bone mineral density LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on Molecular Pharmacology of GPCRs. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v175.21/issuetoc.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biased allosteric modulation at the CaS receptor engendered by structurally diverse calcimimetics.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(1):185-200. doi: 10.1111/bph.12937. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25220431 Free PMC article.
-
Calcimimetic and calcilytic therapies for inherited disorders of the calcium-sensing receptor signalling pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;175(21):4083-4094. doi: 10.1111/bph.14086. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29127708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strontium ranelate decreases receptor activator of nuclear factor-ΚB ligand-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro: involvement of the calcium-sensing receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;78(4):569-76. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.063347. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20584969
-
Vascular actions of calcimimetics: role of Ca²(+) -sensing receptors versus Ca²(+) influx through L-type Ca²(+) channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):749-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01079.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20958288 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulators of the extracellular calcium receptor.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013 Summer;10(2):e277-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2012.11.002. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013. PMID: 24050279 Review.
Cited by
-
Strontium Binding to α-Parvalbumin, a Canonical Calcium-Binding Protein of the "EF-Hand" Family.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1158. doi: 10.3390/biom11081158. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439824 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Simvastatin-Strontium-Hydroxyapatite Coated Implant Formed by Micro-Arc Oxidation and Immersion Method on Osteointegration in Osteoporotic Rabbits.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Mar 16;15:1797-1807. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S244815. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32214812 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Action Calcium-Sensing Receptor Modulator Unmasks Novel Mode-Switching Mechanism.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2018 Sep 12;1(2):96-109. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.8b00021. eCollection 2018 Nov 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 32219206 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of osteogenic properties of a novel injectable bone-repair material containing strontium in vitro and in vivo.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 19;12:1390337. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1390337. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38707496 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Strategies in Osteoporosis: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 23;12(8):1635. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081635. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aurelio L, Valant C, Flynn BL, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A, Scammells PJ (2009). Allosteric modulators of the adenosine A1 receptor: synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 4‐substituted 2‐amino‐3‐benzoylthiophenes. J Med Chem 52: 4543–4547. - PubMed
-
- Bain S, Jerome C, Shen V, Dupin‐Roger I, Ammann P (2009). Strontium ranelate improves bone strength in ovariectomized rat by positively influencing bone resistance determinants. Osteoporos Int 20: 1417–1428. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Tsouderos Y (2002). In vitro effects of S12911‐2 on osteoclast function and bone marrow macrophage differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol 450: 11–17. - PubMed
-
- Boissy P, Saltel F, Bouniol C, Jurdic P, Machuca‐Gayet I (2002). Transcriptional activity of nuclei in multinucleated osteoclasts and its modulation by calcitonin. Endocrinology 143: 1913–1921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

