Cell-cell communication via ciliary extracellular vesicles: clues from model systems
- PMID: 29717060
- PMCID: PMC6922582
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20170085
Cell-cell communication via ciliary extracellular vesicles: clues from model systems
Abstract
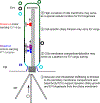
In this short review, we will focus on the uniqueness of ciliary extracellular vesicles (EVs). In particular, we will review what has been learned regarding EVs produced by cilia of model organisms. Model systems including Chlamydomonas, Caenorhabditis elegans, and mouse revealed the fundamental biology of cilia and flagella and provide a paradigm to understand the roles of cilia and flagella in human development, health, and disease. Likewise, we propose that general principles learned from model systems regarding ciliary EV biogenesis and functions may provide a framework to explore the roles of ciliary EVs in human development, health, and disease.
Keywords: C. elegans; cilia; ectosome; extracellular vesicles; microparticles; polycystin.
© 2018 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

