High frequency neural spiking and auditory signaling by ultrafast red-shifted optogenetics
- PMID: 29717130
- PMCID: PMC5931537
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04146-3
High frequency neural spiking and auditory signaling by ultrafast red-shifted optogenetics
Abstract
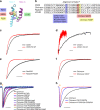
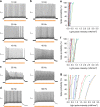
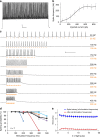
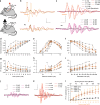
Optogenetics revolutionizes basic research in neuroscience and cell biology and bears potential for medical applications. We develop mutants leading to a unifying concept for the construction of various channelrhodopsins with fast closing kinetics. Due to different absorption maxima these channelrhodopsins allow fast neural photoactivation over the whole range of the visible spectrum. We focus our functional analysis on the fast-switching, red light-activated Chrimson variants, because red light has lower light scattering and marginal phototoxicity in tissues. We show paradigmatically for neurons of the cerebral cortex and the auditory nerve that the fast Chrimson mutants enable neural stimulation with firing frequencies of several hundred Hz. They drive spiking at high rates and temporal fidelity with low thresholds for stimulus intensity and duration. Optical cochlear implants restore auditory nerve activity in deaf mice. This demonstrates that the mutants facilitate neuroscience research and future medical applications such as hearing restoration.
Conflict of interest statement
E.B., T.Ma., T. Mo., P.G.W. and D.L.M. declare no competing non-financial interests but the following competing financial interests. E.B., T.Ma., T. Mo., P.G.W. and D.L.M. are authors on a pending world patent application related to this work, filed by Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften E.V. and Universitaetsmedizin Goettingen (application no. PCT/EP2017/063458; priority date, June 3th 2016). E.B., P.G.W. and T.Ma. are authors on a pending world patent application related to this work, filed by Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften E.V. (application no. PCT/EP2017/063425; priority date, June 3th2016). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Speedy optogenetics in red.Nat Methods. 2018 Jul;15(7):482. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0065-4. Nat Methods. 2018. PMID: 29967501 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

