Diverse developmental pathways of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes
- PMID: 29717233
- PMCID: PMC6063796
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-018-0013-7
Diverse developmental pathways of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes
Abstract
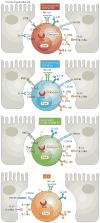
The intestinal epithelial barrier is patrolled by resident intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) that are involved in host defence against pathogens, wound repair and homeostatic interactions with the epithelium, microbiota and nutrients. Intestinal IELs are one of the largest populations of lymphocytes in the body and comprise several distinct subsets, the identity and lineage relationships of which have long remained elusive. Here, we review advances in unravelling the complexity of intestinal IEL populations, which comprise conventional αβ T cell receptor (TCRαβ)+ subsets, unconventional TCRαβ+ and TCRγδ+ subsets, group 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1s) and ILC1-like cells. Although these intestinal IEL lineages have partially overlapping effector programmes and recognition properties, they have strikingly different developmental pathways. We suggest that evolutionary pressure has driven the recurrent generation of cytolytic effector lymphocytes to protect the intestinal epithelial layer, but they may also precipitate intestinal inflammatory disorders, such as coeliac disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Poussier P, Edouard P, Lee C, Binnie M, Julius M. Thymus-independent development and negative selection of T cells expressing T cell receptor αβ in the intestinal epithelium: evidence for distinct circulation patterns of gut-and thymus-derived T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992;176:187–199. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abadie V, Discepolo V, Jabri B. Intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol. 2012;34:551–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

