Myoediting: Toward Prevention of Muscular Dystrophy by Therapeutic Genome Editing
- PMID: 29717930
- PMCID: PMC6335101
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00046.2017
Myoediting: Toward Prevention of Muscular Dystrophy by Therapeutic Genome Editing
Abstract
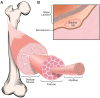
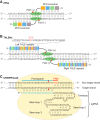
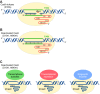
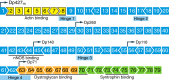
Muscular dystrophies represent a large group of genetic disorders that significantly impair quality of life and often progress to premature death. There is no effective treatment for these debilitating diseases. Most therapies, developed to date, focus on alleviating the symptoms or targeting the secondary effects, while the underlying gene mutation is still present in the human genome. The discovery and application of programmable nucleases for site-specific DNA double-stranded breaks provides a powerful tool for precise genome engineering. In particular, the CRISPR/Cas system has revolutionized the genome editing field and is providing a new path for disease treatment by targeting the disease-causing genetic mutations. In this review, we provide a historical overview of genome-editing technologies, summarize the most recent advances, and discuss potential strategies and challenges for permanently correcting genetic mutations that cause muscular dystrophies.
Figures



References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Van Deutekom JC, Fokkema IF, Van Ommen GJ, Den Dunnen JT. Entries in the Leiden Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutation database: an overview of mutation types and paradoxical cases that confirm the reading-frame rule. Muscle Nerve 34: 135–144, 2006. doi:10.1002/mus.20586. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abudayyeh OO, Gootenberg JS, Konermann S, Joung J, Slaymaker IM, Cox DB, Shmakov S, Makarova KS, Semenova E, Minakhin L, Severinov K, Regev A, Lander ES, Koonin EV, Zhang F. C2c2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector. Science 353: aaf5573, 2016. doi:10.1126/science.aaf5573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

