Favorable glycemic response after pancreatoduodenectomy in both patients with pancreatic cancer and patients with non-pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 29718860
- PMCID: PMC6393016
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010590
Favorable glycemic response after pancreatoduodenectomy in both patients with pancreatic cancer and patients with non-pancreatic cancer
Abstract
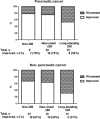
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is prevalent in patients with pancreatic cancer and tends to improve after tumor resection. However, the glycemic response of non-pancreatic cancer patients after surgery has not been examined in detail. We aimed to investigate the changes in glucose metabolism in patients with pancreatic cancer or non-pancreatic cancer after pancreatoduodenectomy (PD).We prospectively enrolled 48 patients with pancreatic cancer and 56 patients with non-pancreatic cancer, who underwent PD. Glucose metabolism was assessed with fasting glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), plasma C-peptide and insulin, quantitative insulin check index (QUICKI), and a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and β cell (HOMA-β) before surgery and 6 months after surgery. Patients were divided into 2 groups: "improved" and "worsened" postoperative glycemic response, according to the changes in HbA1c and anti-diabetic medication. New-onset DM was defined as diagnosis of DM ≤ 2 years before PD, and cases with DM diagnosis >2 years preceding PD were described as long-standing DM.After PD, insulin resistance (IR), as measured by insulin, HOMA-IR and QUICKI, improved significantly, although C-peptide and HOMA-β decreased. At 6 months after PD, new-onset DM patients showed improved glycemic control in both pancreatic cancer patients (75%) and non-pancreatic cancer patients (63%). Multivariate analysis showed that long-standing DM was a significant predictor for worsening glucose control (odds ratio = 4.01, P = .017).Favorable glycemic control was frequently observed in both pancreatic cancer and non-pancreatic cancer after PD. PD seems to contribute improved glucose control through the decreased IR. New-onset DM showed better glycemic control than long-standing DM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Noy A, Bilezikian JP. Clinical review 63: Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: clues to the early diagnosis of pancreatic malignancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;79:1223–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

