Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 29719179
- PMCID: PMC6776074
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706441
Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques in the brain. Aβ is produced from the sequential cleavage of amyloid precursor protein by β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) followed by γ-secretase. Verubecestat is an oral BACE-1 inhibitor that reduces the Aβ level in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease.
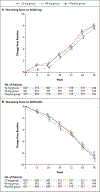
Methods: We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 78-week trial to evaluate verubecestat at doses of 12 mg and 40 mg per day, as compared with placebo, in patients who had a clinical diagnosis of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. The coprimary outcomes were the change from baseline to week 78 in the score on the cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog; scores range from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating worse dementia) and in the score on the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living Inventory scale (ADCS-ADL; scores range from 0 to 78, with lower scores indicating worse function).
Results: A total of 1958 patients underwent randomization; 653 were randomly assigned to receive verubecestat at a dose of 12 mg per day (the 12-mg group), 652 to receive verubecestat at a dose of 40 mg per day (the 40-mg group), and 653 to receive matching placebo. The trial was terminated early for futility 50 months after onset, which was within 5 months before its scheduled completion, and after enrollment of the planned 1958 patients was complete. The estimated mean change from baseline to week 78 in the ADAS-cog score was 7.9 in the 12-mg group, 8.0 in the 40-mg group, and 7.7 in the placebo group (P=0.63 for the comparison between the 12-mg group and the placebo group and P=0.46 for the comparison between the 40-mg group and the placebo group). The estimated mean change from baseline to week 78 in the ADCS-ADL score was -8.4 in the 12-mg group, -8.2 in the 40-mg group, and -8.9 in the placebo group (P=0.49 for the comparison between the 12-mg group and the placebo group and P=0.32 for the comparison between the 40-mg group and the placebo group). Adverse events, including rash, falls and injuries, sleep disturbance, suicidal ideation, weight loss, and hair-color change, were more common in the verubecestat groups than in the placebo group.
Conclusions: Verubecestat did not reduce cognitive or functional decline in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease and was associated with treatment-related adverse events. (Funded by Merck; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01739348 .).
Figures
Comment in
-
[Journal Club].Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jul;51(5):597-599. doi: 10.1007/s00391-018-1416-6. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 29948153 German. No abstract available.
-
New treatments in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol. 2018 Sep;265(9):2162-2163. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9018-1. J Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30132064 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
