Descending Inputs to Spinal Circuits Facilitating and Inhibiting Human Wrist Flexors
- PMID: 29719504
- PMCID: PMC5913321
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00147
Descending Inputs to Spinal Circuits Facilitating and Inhibiting Human Wrist Flexors
Abstract
Recently we reported in humans that electrical stimulation of the wrist extensor muscle extensor carpi radialis (ECR) could facilitate or suppress the H reflex elicited in flexor carpi radialis (FCR), for inter-stimulus intervals (ISIs) of 30 ms or 70 ms, respectively. The facilitation at 30 ms may be produced by both flexor afferents and extensor Ib afferents acting on a spinal circuit; the origin of the suppression at 70 ms is less certain. In this study, we investigated possible descending inputs to these systems. We used magnetic stimulation of the contralateral primary motor cortex, and click sound stimulation, to activate the corticospinal and the reticulospinal tracts respectively, and measured the effects on the H reflex conditioned by ECR stimulation. Corticospinal inputs reduced both the 30 ms facilitation and 70 ms suppression, indicating corticospinal inhibition of both circuits. By contrast, we failed to show any effect of clicks, either on the H reflex or on its modulation by ECR stimulation. This suggests that click-activated reticulospinal inputs to these circuits may be weak or absent.
Keywords: H-reflex; Ib afferents; click sound stimulation; corticospinal tract; reticulospinal tract; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Figures
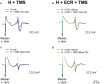
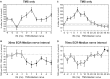
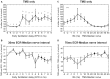
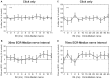

Similar articles
-
Temporal Profile of Descending Cortical Modulation of Spinal Excitability: Group and Individual-Specific Effects.Front Integr Neurosci. 2022 Jan 7;15:777741. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2021.777741. eCollection 2021. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35197831 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent Spinal Circuits Facilitating Human Wrist Flexors.J Neurosci. 2018 Apr 18;38(16):3929-3938. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1870-17.2018. Epub 2018 Mar 21. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29563182 Free PMC article.
-
Task dependent gain regulation of spinal circuits projecting to the human flexor carpi radialis.Exp Brain Res. 2005 Mar;161(3):299-306. doi: 10.1007/s00221-004-2072-1. Epub 2004 Nov 13. Exp Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15551085
-
Oligosynaptic inhibition mediated by group Ia afferents from flexor digitorum superficialis to wrist flexors in humans.Exp Brain Res. 2018 Jul;236(7):1849-1860. doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5268-5. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Exp Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29679107
-
Contributions to the understanding of gait control.Dan Med J. 2014 Apr;61(4):B4823. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24814597 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Assessment of Hand Spasticity After Stroke: Imaging Correlates and Impact on Motor Recovery.Front Neurol. 2019 Aug 12;10:836. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00836. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31456734 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of central lesions on a spinal circuit facilitating human wrist flexors.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 4;8(1):14821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33012-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30287827 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Profile of Descending Cortical Modulation of Spinal Excitability: Group and Individual-Specific Effects.Front Integr Neurosci. 2022 Jan 7;15:777741. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2021.777741. eCollection 2021. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35197831 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

