C-Cbl reverses HER2-mediated tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29720121
- PMCID: PMC5930956
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4387-5
C-Cbl reverses HER2-mediated tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
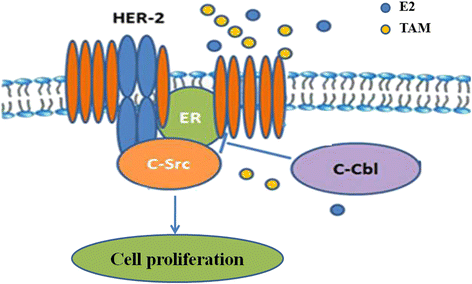
Background: Tamoxifen is a frontline therapy for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer in premenopausal women. However, many patients develop resistance to tamoxifen, and the mechanism underlying tamoxifen resistance is not well understood. Here we examined whether ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation is involved in tamoxifen resistance.
Methods: MTT and colony formation assays were used to measure cell viability and proliferation. Western blot was used to detect protein expression and protein complex formations were detected by immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence. SiRNA was used to examine the function of HER2 in of BT474 cells. An in vivo xenograft animal model was established to examine the role of c-Cbl in tumor growth.
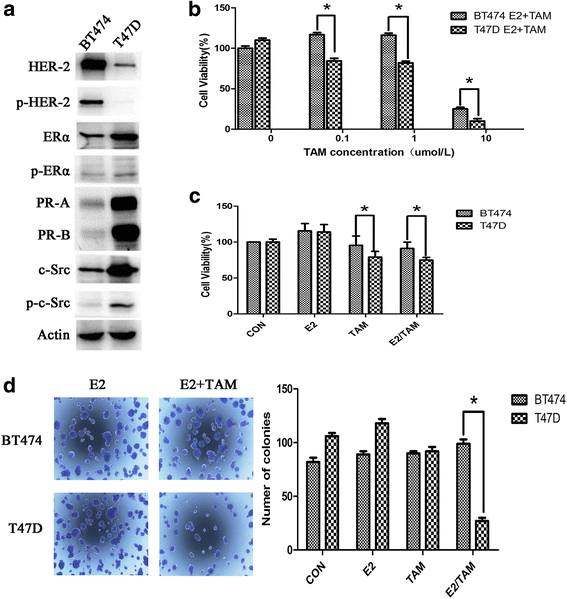
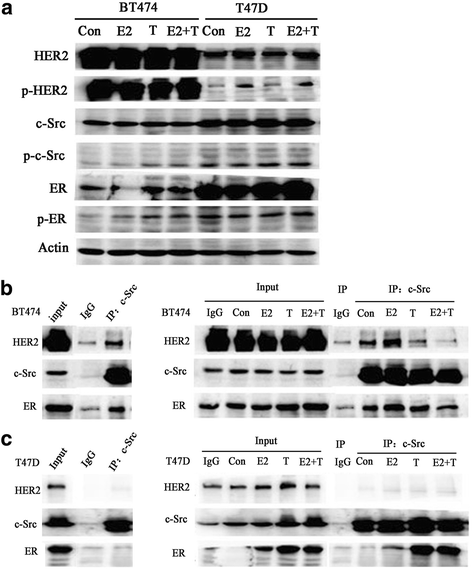
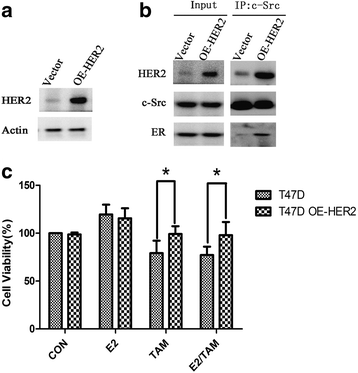
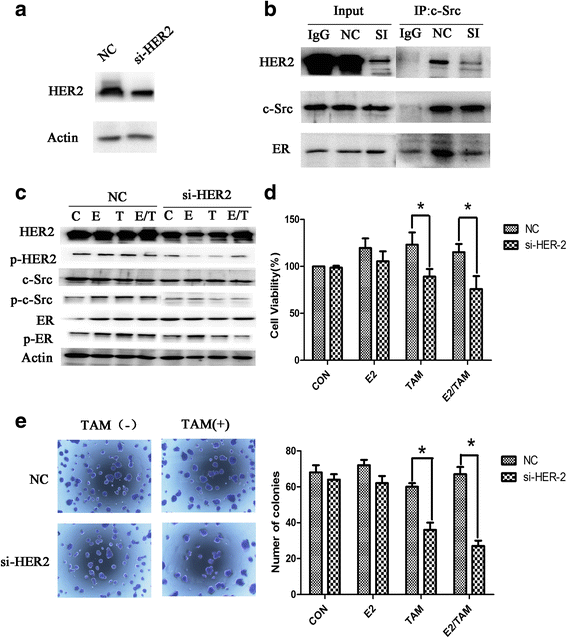
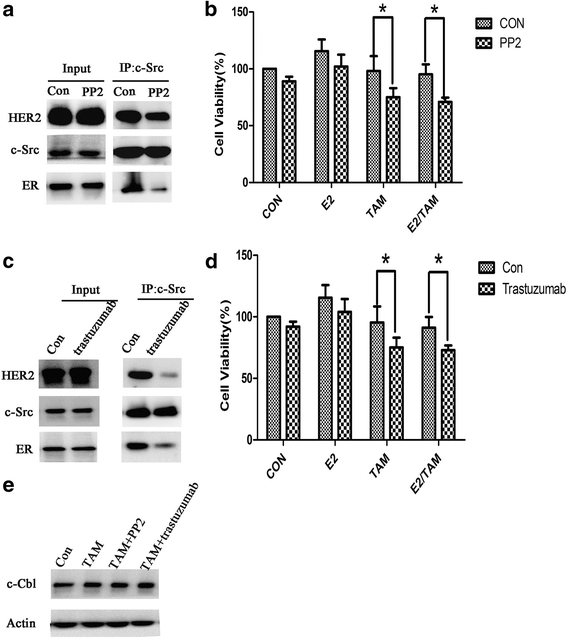
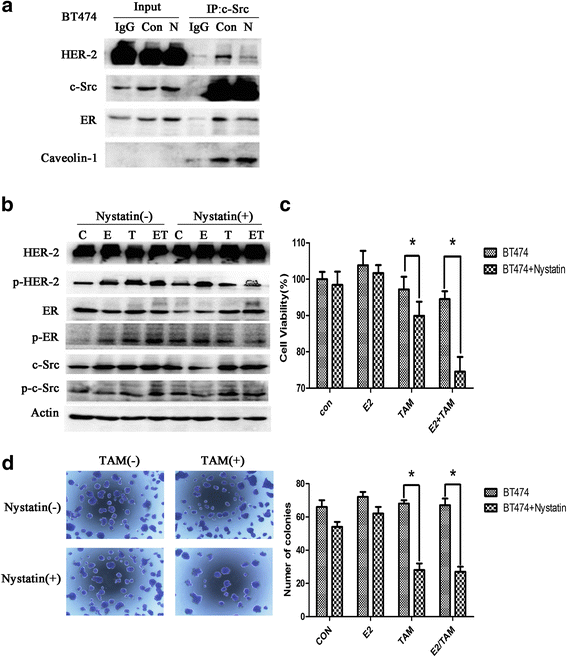
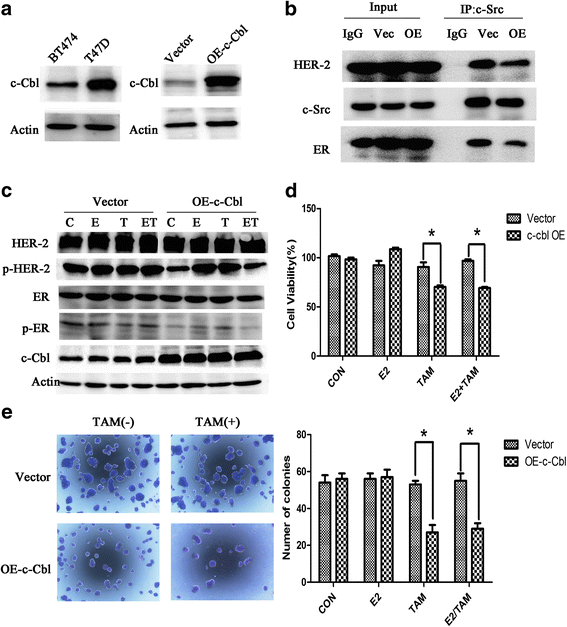
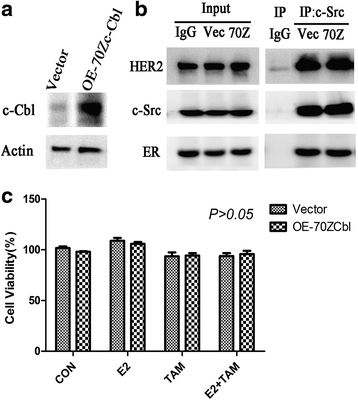
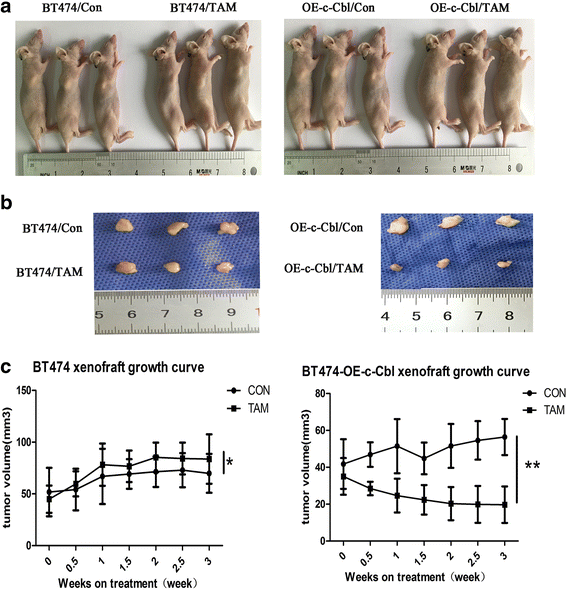
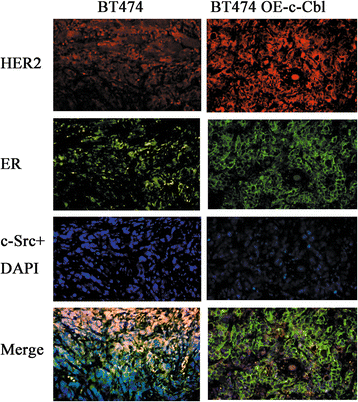
Results: MTT and colony formation assay showed that BT474 cells are resistant to tamoxifen and T47D cells are sensitive to tamoxifen. Immunoprecipitation experiments revealed ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation in BT474 cells but not in T47D cells. However, ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation was detected after overexpressing HER2 in T47D cells and these cells were more resistant to tamoxifen. HER2 knockdown by siRNA in BT474 cells reduced ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation and reversed tamoxifen resistance. ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation was also disrupted and tamoxifen resistance was reversed in BT474 cells by the c-Src inhibitor PP2 and HER2 antibody trastuzumab. Nystatin, a lipid raft inhibitor, reduced ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation and partially reversed tamoxifen resistance. ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation was disrupted by overexpression of c-Cbl but not by the c-Cbl ubiquitin ligase mutant. In addition, c-Cbl could reverse tamoxifen resistance in BT474 cells, but the ubiquitin ligase mutant had no effect. The effect of c-Cbl was validated in BT474 tumor-bearing nude mice in vivo. Immunofluorescence also revealed ER-c-Src-HER2 complex formation was reduced in tumor tissues of nude mice with c-Cbl overexpression.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that c-Cbl can reverse tamoxifen resistance in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by inhibiting the formation of the ER-c-Src-HER2 complex.
Keywords: Breast cancer; C-Cbl; HER2; Resistance; Tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We required ethics approval for the use of cell lines used in this study. Ethical approval was given by the Medical Science Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University (reference number 201121). The animal experiments were approved by the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection Committee of Laboratory Animal Center, China Medical University (reference number 15018 M).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

