Interferon regulatory factor 1 and a variant of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L coordinately silence the gene for adhesion protein CEACAM1
- PMID: 29720400
- PMCID: PMC6005424
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001507
Interferon regulatory factor 1 and a variant of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L coordinately silence the gene for adhesion protein CEACAM1
Abstract
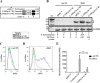
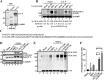
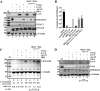
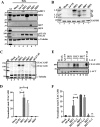
The adhesion protein carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) is widely expressed in epithelial cells as a short cytoplasmic isoform (S-iso) and in leukocytes as a long cytoplasmic isoform (L-iso) and is frequently silenced in cancer by unknown mechanisms. Previously, we reported that interferon response factor 1 (IRF1) biases alternative splicing (AS) to include the variable exon 7 (E7) in CEACAM1, generating long cytoplasmic isoforms. We now show that IRF1 and a variant of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (Lv1) coordinately silence the CEACAM1 gene. RNAi-mediated Lv1 depletion in IRF1-treated HeLa and melanoma cells induced significant CEACAM1 protein expression, reversed by ectopic Lv1 expression. The Lv1-mediated CEACAM1 repression resided in residues Gly71-Gly89 and Ala38-Gly89 in Lv1's N-terminal extension. ChIP analysis of IRF1- and FLAG-tagged Lv1-treated HeLa cells and global treatment with the global epigenetic modifiers 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and trichostatin A indicated that IRF1 and Lv1 together induce chromatin remodeling, restricting IRF1 access to the CEACAM1 promoter. In interferon γ-treated HeLa cells, the transcription factor SP1 did not associate with the CEACAM1 promoter, but binding by upstream transcription factor 1 (USF1), a known CEACAM1 regulator, was greatly enhanced. ChIP-sequencing revealed that Lv1 overexpression in IRF1-treated cells induces transcriptional silencing across many genes, including DCC (
Keywords: CEACAM1; IFN-gamma; IRF1; RNA; alternative splicing; chromatin remodeling; hnRNP L; transcription; translation regulation.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Chao, C. H., Chen, C. M., Cheng, P. L., Shih, J. W., Tsou, A. P., and Lee, Y. H. (2006) DDX3, a DEAD box RNA helicase with tumor growth-suppressive property and transcriptional regulation activity of the p21waf1/cip1 promoter, is a candidate tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 66, 6579–6588 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2415 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simon, J. M., Hacker, K. E., Singh, D., Brannon, A. R., Parker, J. S., Weiser, M., Ho, T. H., Kuan, P. F., Jonasch, E., Furey, T. S., Prins, J. F., Lieb, J. D., Rathmell, W. K., and Davis, I. J. (2014) Variation in chromatin accessibility in human kidney cancer links H3K36 methyltransferase loss with widespread RNA processing defects. Genome Res. 24, 241–250 10.1101/gr.158253.113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

