Efficacy and safety profile of xanthines in COPD: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 29720510
- PMCID: PMC9488859
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0010-2018
Efficacy and safety profile of xanthines in COPD: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
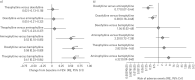
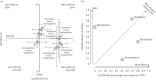
Theophylline can still have a role in the management of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but its use remains controversial, mainly due to its narrow therapeutic window. Doxofylline, another xanthine, is an effective bronchodilator and displays a better safety profile than theophylline. Therefore, we performed a quantitative synthesis to compare the efficacy and safety profile of different xanthines in COPD.The primary end-point of this meta-analysis was the impact of xanthines on lung function. In addition, we assessed the risk of adverse events by normalising data on safety as a function of person-weeks. Data obtained from 998 COPD patients were selected from 14 studies and meta-analysed using a network approach.The combined surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) analysis of efficacy (change from baseline in forced expiratory volume in 1 s) and safety (risk of adverse events) showed that doxofylline was superior to aminophylline (comparable efficacy and significantly better safety), bamiphylline (significantly better efficacy and comparable safety), and theophylline (comparable efficacy and significantly better safety).Considering the overall efficacy/safety profile of the investigated agents, the results of this quantitative synthesis suggest that doxofylline seems to be the best xanthine for the treatment of COPD.
Copyright ©ERS 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Cazzola reports personal fees from ABC Farmaceutici, outside the submitted work, and received personal fees to perform the meta-analysis and write the article. Conflict of interest: L. Calzetta reports personal fees from ABC Farmaceutici, during the conduct of the study, and received personal fees to perform the meta-analysis and write the article. Conflict of interest: M.G. Matera reports personal fees from ABC Farmaceutici, outside the submitted work. She is also a consultant at ABC Farmaceutici and was supported to write the article.
Figures
References
-
- Barnes PJ. Theophylline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013; 188: 901–906. - PubMed
-
- Taylor DR, Buick B, Kinney C, et al. . The efficacy of orally administered theophylline, inhaled salbutamol, and a combination of the two as chronic therapy in the management of chronic bronchitis with reversible air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis 1985; 131: 747–751. - PubMed
-
- Murciano D, Auclair MH, Pariente R, et al. . A randomized, controlled trial of theophylline in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 1521–1525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
