[Can medical students' motivation for a course of basic physiology education integrating into lectures some active learning methods be improved?]
- PMID: 29721145
- PMCID: PMC5927575
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2017.28.315.10251
[Can medical students' motivation for a course of basic physiology education integrating into lectures some active learning methods be improved?]
Abstract
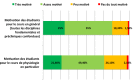
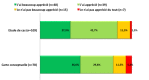
Students' motivation is a critical component of learning and students' perception of activity value is one of the three major components of their motivation. How can we make students perceive the usefulness and the interest of their university courses while increasing their motivation? The aim of our study was to determine students' perception of basic physiology education value and to assess the impact of lecture integration into some active learning methods on the motivation of the students of the first cycle of Medicine in a junior faculty. We conducted a prospective study, involving the students in their second year of medical studies. At first, we assessed students' motivation for university courses through a first questionnaire, after we integrated two educational activities: the case study and the realization of a conceptual map for the lectures of the physiology module and then we evaluated, through a second questionnaire, the impact of these two activities on students' motivation. Out of 249 students in their second year of medical studies 131 and 109 students have completed and returned the 1st and 2nd questionnaire respectively. Overall students' motivation for their university courses was very favorable, even if the motivation for physiology course (70.8%) was slightly lower than for all the courses (80%). Our students enjoyed the two proposed activities and only 13% (for the case study) and 16.8% (for the map) were not satisfied. 40.9% of students completed a conceptual map whose quality judged on the identification of concepts and of the links between concepts was globally satisfactory for a first experience. Students' motivation is influenced by multiple internal and external factors and is a big problem in the university environment. In this context, a rigorous planning of diversified and active educational activities is one of the main gateways for teacher to encourage motivation.
La motivation des étudiants est une condition essentielle à l’apprentissage et la perception qu’a l’étudiant de la valeur qu’il accorde à une activité est l’une des trois composantes majeures de cette motivation. Comment amener les étudiants à percevoir l’utilité et l’intérêt de leurs cours universitaires tout en suscitant leur motivation ? L’objectif de l’étude est de déterminer la perception de la valeur attribuée par les étudiants au cours fondamental de physiologie et d’évaluer l’impact de l’intégration de quelques méthodes d’apprentissage actif aux exposés magistraux sur la motivation des étudiants du premier cycle des études médicales dans une jeune faculté. Cette étude prospective, a concerné les étudiants de deuxième année de médecine (PCEM2). Nous avons procédé initialement à une appréciation de la perception de la motivation des étudiants pour les cours universitaires via un premier questionnaire, après nous avons intégré deux activités pédagogiques: l’étude de cas et la réalisation de carte conceptuelle aux exposés magistraux du module de physiologie et à la fin nous avons évalué via un deuxième questionnaire l’impact de ces deux activités sur la motivation des étudiants. 131 et 109 étudiants ont rempli et rendu respectivement le 1er et le 2ème questionnaire parmi les 249 étudiants inscrits en PCEM2. La motivation de nos étudiants à l’égard de leurs cours universitaires était globalement très favorable, même si la motivation pour le cours de physiologie (70,8%) était légèrement moins importante que pour l’ensemble des cours (80%). Nos étudiants avaient apprécié les deux activités proposées et seulement 13% (pour l’étude de cas) et 16,8% (pour la carte) ne se montraient pas satisfaits. 40,9% des étudiants avaient réalisé une carte conceptuelle et la qualité de ces productions, jugée sur l’identification des concepts et des liens inter concepts, était globalement satisfaisante pour une première expérience. Influencée par de multiples facteurs internes et externes, la motivation des étudiants reste une grande problématique en milieu universitaire. Dans ce contexte, une planification rigoureuse d’activités pédagogiques diversifiées et actives est l’une des principales portes offertes à l’enseignant pouvant susciter cette motivation.
Keywords: Motivation; basic education; case study; conceptual map; medical studies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated problem-based learning versus lectures: a path analysis modelling of the relationships between educational context and learning approaches.Med Educ Online. 2018 Dec;23(1):1489690. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2018.1489690. Med Educ Online. 2018. PMID: 29966510 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive Lecture in the Dissection Hall: Transforming Passive Lecture into a Dynamic Learning Experience.Anat Sci Educ. 2019 Mar;12(2):191-199. doi: 10.1002/ase.1803. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Anat Sci Educ. 2019. PMID: 30118568
-
Team-Based Learning Activities for First-Year Medical Students: Perception of the Learners.South Med J. 2018 Sep;111(9):525-529. doi: 10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000865. South Med J. 2018. PMID: 30180247
-
Teaching Animal Physiology: a 12-year experience transitioning from a classical to interactive approach with continual assessment and computer alternatives.Adv Physiol Educ. 2017 Sep 1;41(3):405-414. doi: 10.1152/advan.00132.2016. Adv Physiol Educ. 2017. PMID: 28679579 Review.
-
Andragogy and medical education: are medical students internally motivated to learn?Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2002;7(2):153-60. doi: 10.1023/a:1015790318032. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2002. PMID: 12075147 Review.
Cited by
-
Lebanese students' motivation in medical school: does it change throughout the years? A cross-sectional study.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Mar 31;20(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02011-w. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 32234030 Free PMC article.
-
Distant education in Moroccan medical schools following COVID-19 outbreak at the early phase of lockdown: Were the students really engaged?Sci Afr. 2022 Mar;15:e01087. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01087. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Sci Afr. 2022. PMID: 34977441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Viau R. La motivation en contexte scolaire. St-Laurent (Québec). Éditions du Renouveau pédagogique; 1994.
-
- Wigefield A, et Eccles JS. The development of achievement task values: a theoretical analysis. Develop mental review. 1992;12:265–310.
-
- Bandura A. Perceived self-efficacity in cognitive development and functionning. Educational Psychologist. 1993;28:117–148.
-
- Bouffard-Bouchard T, Parent S, Larivée S. Influence of self-efficacity on self-regulation and performance among junior and senior high school age students. International Journal of Behavioral Development. 1991;14:153–164.
-
- Pajares F. Self-efficacity beliefs in academic setting. Review of Educationnal Research. 1996;66:543–578.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
