Assessment of micro RNAs expression in leukemic cells as prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: micro RNAs can predict survival in a course of the disease
- PMID: 29721189
- PMCID: PMC5922383
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24927
Assessment of micro RNAs expression in leukemic cells as prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: micro RNAs can predict survival in a course of the disease
Abstract
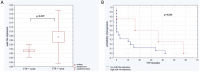
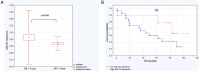
Numerous genetic alterations predicting prognosis and clinical outcome are revealed recently in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Among them the deregulated expression of micro RNAs that can induce tumor growth, or act as tumor suppressors seem to be of great importance. This study aimed to analyze the possible role of chosen micro RNAs as markers of prognosis in patients with CLL. We assessed the expression of miR-21, miR-34a, miR-181a, miR-199a/b and miR-221 in previously separated leukemic cells with the use of qRQ-PCR technique at the moment of diagnosis. The results were then analyzed in regards to presence of prognostic factors, clinical data and the end points like progression free survival (PFS), time to progression (TP) and overall survival time (OS). We detected significant correlations between expression of the analyzed micro RNAs and CLL prognostic markers particularly as far as miR-221 and miR-181a were concerned. The subsequent analysis revealed that high expression of miR-34a and miR-181a as well as low miR-21 expression indicated longer TTP, while miR-221 was predictor of OS. The obtained results prove the role of micro RNAs as CLL prognostic markers, particularly as factors predicting survival in a course of the disease.
Keywords: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; micro RNA; overall survival; prognostic factors; progression free survival.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There were no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, et al. Frequent deletions and downregulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–15529. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamblin TJ, Oscier DG. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the nature of the leukemic cells. Blood Rev. 1997;11:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M. Therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2010;23:85–96. - PubMed
-
- Furman RR. Prognostic markers and stratification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010;2010:77–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

