Circulating and tumor-associated caspase-4: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29721208
- PMCID: PMC5922402
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25049
Circulating and tumor-associated caspase-4: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Circulating and tumor-associated caspase-4: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Jun 29;9(50):29537. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25751. eCollection 2018 Jun 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30034638 Free PMC article.
Abstract
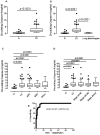
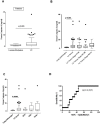
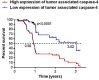
Late diagnosis limits therapeutic options and survival rate of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Therefore the identification of biomarkers represents an emerging medical need. A highly sensitive and specific test was developed to identify/quantify a novel/selective diagnostic biomarker for NSCLC patients, caspase-4. This test was validated by using i) plasma from 125 NSCLC patients and 79 healthy (non-pathological) subjects, ii) plasma from 139 smokers and iii) from 70 chronic-obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients. Caspase-4 quantification was also assessed in the lung tumor mass of 98 paired NSCLC patients compared to 10 non-tumor lung tissues (i.e. tuberculosis). Circulating caspase-4 was detected in both healthy and NSCLC patients; however at different range values: 2.603-3.372 ng/ml for NSCLC patients (95% CI) compared to 0.3994-0.6219 ng/ml for healthy subjects (95% CI). The sensitivity of the test ranged from 97.07% to 100%; the specificity was 88.1% with a positive predictive value of 92.54%, accuracy of 95.19% and AUC of 0.971. Smokers (95% CI, 0.3947-0.6197 ng/ml) and COPD patients (95% CI, 1.703-2.995 ng/ml) showed intermediate values of circulating caspase-4. Tissue levels of caspase-4 in the tumor mass showed that 72 (72.7%) out of 99 patients were positive. More importantly, higher levels (cut-off value = 0.307 ng/ml) of caspase-4 in the tumor mass were associated to reduced overall survival (median 0.92 years) compared to NSCLC patients with lower levels (median 3.02 years). We report for the first time caspase-4 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker, opening new therapeutic perspectives for NSCLC patients.
Keywords: NSCLC; biomarker; diagnosis; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST MT, RPA, AP, AS and RS are co-founders of ImmunePharma S.r.l., academic spin-off at the University of Salerno, Department of Pharmacy (DIFARMA). ImmunePharma S.r.l. counts on the following patents: RM2014A000080 and PCT/IB2015/051262. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ, Jr, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Franklin WA, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA., Jr Early Detection of Lung Cancer: Clinical Perspectives of Recent Advances in Biology and Radiology. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:5–22. - PubMed
-
- Rizvi NA, Peters S. Immunotherapy for Unresectable Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1986–1988. - PubMed
-
- Jett JR. Limitations of screening for lung cancer with low-dose spiral computed tomography. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4988s–4992s. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

