Vildagliptin Can Alleviate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Liver Induced by a High Fat Diet
- PMID: 29721506
- PMCID: PMC5867538
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5045182
Vildagliptin Can Alleviate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Liver Induced by a High Fat Diet
Abstract
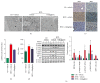
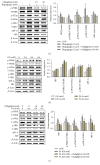
Purpose. We investigated whether a DDP-4 inhibitor, vildagliptin, alleviated ER stress induced by a high fat diet and improved hepatic lipid deposition. Methods. C57BL/6 mice received standard chow diet (CD), high fat diet (HFD), and HFD administered with vildagliptin (50 mg/Kg) (V-HFD). After administration for 12 weeks, serum alanine aminotransferase, glucose, cholesterol, triglyceride, and insulin levels were analyzed. Samples of liver underwent histological examination and transmission electron microscopy, real-time PCR for gene expression levels, and western blots for protein expression levels. ER stress was induced in HepG2 cells with palmitic acid and the effects of vildagliptin were investigated. Results. HFD mice showed increased liver weight/body weight (20.27%) and liver triglycerides (314.75%) compared to CD mice, but these decreased by 9.27% and 21.83%, respectively, in V-HFD mice. In the liver, HFD induced the expression of ER stress indicators significantly, which were obviously decreased by vildagliptin. In vitro, the expressions of molecular indicators of ER stress were reduced in HepG2 when vildagliptin was administered. Conclusions. Vildagliptin alleviates hepatic ER stress in a mouse high fat diet model. In HepG2 cells, vildagliptin directly reduced ER stress. Therefore, vildagliptin may be a potential agent for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures


References
-
- Read P. A., Khan F. Z., Heck P. M., Hoole S. P., Dutka D. P. DPP-4 inhibition by sitagliptin improves the myocardial response to dobutamine stress and mitigates stunning in a pilot study of patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2010;3(2):195–201. doi: 10.1161/circimaging.109.899377. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

