Functional and evolutionary analysis of viral proteins containing a Rossmann-like fold
- PMID: 29722076
- PMCID: PMC6153405
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3438
Functional and evolutionary analysis of viral proteins containing a Rossmann-like fold
Abstract
Viruses are the most abundant life form and infect practically all organisms. Consequently, these obligate parasites are a major cause of human suffering and economic loss. Rossmann-like fold is the most populated fold among α/β-folds in the Protein Data Bank and proteins containing Rossmann-like fold constitute 22% of all known proteins 3D structures. Thus, analysis of viral proteins containing Rossmann-like domains could provide an understanding of viral biology and evolution as well as could propose possible targets for antiviral therapy. We provide functional and evolutionary analysis of viral proteins containing a Rossmann-like fold found in the evolutionary classification of protein domains (ECOD) database developed in our lab. We identified 81 protein families of bacterial, archeal, and eukaryotic viruses in light of their evolution-based ECOD classification and Pfam taxonomy. We defined their functional significance using enzymatic EC number assignments as well as domain-level family annotations.
Keywords: Rossmann-like fold; evolution; viral proteins.
© 2018 The Protein Society.
Figures

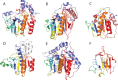
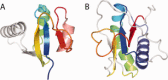
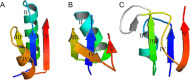
Similar articles
-
A Fifth of the Protein World: Rossmann-like Proteins as an Evolutionarily Successful Structural unit.J Mol Biol. 2021 Feb 19;433(4):166788. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.166788. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33387532 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of Rossmann-like domains reveals convergent evolution of topology and reaction pathways.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Dec 23;15(12):e1007569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007569. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31869345 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the Gap between Sequence and Structure Classifications of Proteins with AlphaFold Models.J Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 15;436(22):168764. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168764. Epub 2024 Aug 26. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39197652
-
What does structure tell us about virus evolution?Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Dec;15(6):655-63. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.10.012. Epub 2005 Nov 3. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 16271469 Review.
-
A protein domain-based view of the virosphere-host relationship.Biochimie. 2015 Dec;119:231-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 26296474 Review.
Cited by
-
Methyltransferases of Riboviria.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 6;12(9):1247. doi: 10.3390/biom12091247. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139088 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Core Postfusion Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus Fusion Protein.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0292021. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02920-21. Epub 2022 Jan 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35073741 Free PMC article.
-
Structural bioinformatic analysis of DsbA proteins and their pathogenicity associated substrates.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Aug 14;19:4725-4737. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.018. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34504665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+-based allosteric switches and shape shifting in RGLG1 VWA domain.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Mar 30;18:821-833. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.03.023. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32308929 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of the nsp14 N7-guanine methyltransferase reveals an essential role in Betacoronavirus replication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Dec 7;118(49):e2108709118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108709118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34845015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Koonin EV (2002) Monophyly of class I aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, USPA, ETFP, photolyase, and PP‐ATPase nucleotide‐binding domains: Implications for protein evolution in the RNA world. Proteins 48:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Berman HM, Bhat TN, Bourne PE, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Weissig H, Westbrook J (2000) The Protein Data Bank and the challenge of structural genomics. Nat Struct Biol 7:957–959. - PubMed
-
- Rossmann MG, Moras D, Olsen KW (1974) Chemical and biological evolution of a nucleotide‐binding protein. Nature 250:194–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

