Comparison of Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels to Simultaneously Obtained Right Heart Hemodynamics in Stable Outpatients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 29723983
- PMCID: PMC6023321
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases6020033
Comparison of Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels to Simultaneously Obtained Right Heart Hemodynamics in Stable Outpatients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
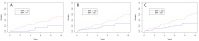
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a progressive disease that requires validated biomarkers of disease severity. While PAH is defined hemodynamically by right heart catheterization (RHC), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is recommended by guidelines to assess disease status. Retrospectively collected data in 138 group 1 PAH patients were examined for the correlation of BNP levels to simultaneously obtained right heart catheterization (RHC). Patients were mostly Caucasian women, with functional class III symptoms, mean BNP of 406 ± 443 pg/mL, and an average right atrial pressure (RAP) of 9.9 ± 5.7 mm Hg and mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 47.3 ± 14.7 mm Hg. Significant correlation was demonstrated between BNP and RAP (p = 0.021) and mPAP (p = 0.003). Additional correlation was seen with right heart size on echocardiography: right atrial (RAE; p = 0.04) and right ventricular enlargement (p = 0.03). An increased BNP level was an independent predictor of mortality (p < 0.0001), along with RAP (p = 0.039) and RAE (p = 0.018). Simultaneous collection of BNP at the time of RHC confirmed the correlation of BNP with right heart hemodynamics. The current results reinforce the use of BNP level as a continuous variable to assess disease severity in group 1 PAH.
Keywords: biomarkers; brain natriuretic peptide; pulmonary arterial hypertension; right heart catheterization; transthoracic echocardiogram.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Benza R.L., Miller D.P., Gomberg-Maitland M., Frantz R.P., Foreman A.J., Coffey C.S., McGoon M.D. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL) Circulation. 2010;122:164–172. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.898122. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galie N., Humbert M., Vachiery J.L., Gibbs S., Lang I., Torbicki A., Hoeper M. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur. Respir. J. 2015;46:903–975. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources