Targeting HSP90 dimerization via the C terminus is effective in imatinib-resistant CML and lacks the heat shock response
- PMID: 29724897
- PMCID: PMC6225350
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-10-810986
Targeting HSP90 dimerization via the C terminus is effective in imatinib-resistant CML and lacks the heat shock response
Abstract
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) stabilizes many client proteins, including the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein. BCR-ABL1 is the hallmark of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in which treatment-free remission (TFR) is limited, with clinical and economic consequences. Thus, there is an urgent need for novel therapeutics that synergize with current treatment approaches. Several inhibitors targeting the N-terminal domain of HSP90 are under investigation, but side effects such as induction of the heat shock response (HSR) and toxicity have so far precluded their US Food and Drug Administration approval. We have developed a novel inhibitor (aminoxyrone [AX]) of HSP90 function by targeting HSP90 dimerization via the C-terminal domain. This was achieved by structure-based molecular design, chemical synthesis, and functional preclinical in vitro and in vivo validation using CML cell lines and patient-derived CML cells. AX is a promising potential candidate that induces apoptosis in the leukemic stem cell fraction (CD34+CD38-) as well as the leukemic bulk (CD34+CD38+) of primary CML and in tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-resistant cells. Furthermore, BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein and related pro-oncogenic cellular responses are downregulated, and targeting the HSP90 C terminus by AX does not induce the HSR in vitro and in vivo. We also probed the potential of AX in other therapy-refractory leukemias. Therefore, AX is the first peptidomimetic C-terminal HSP90 inhibitor with the potential to increase TFR in TKI-sensitive and refractory CML patients and also offers a novel therapeutic option for patients with other types of therapy-refractory leukemia because of its low toxicity profile and lack of HSR.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


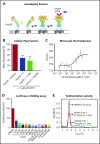


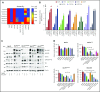
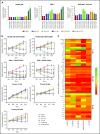

Comment in
-
HSP90 inhibition without heat shock response.Blood. 2018 Jul 19;132(3):241-242. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-850271. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30026301 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition of Bcr-Abl and Hsp90 by C086 potently inhibits the proliferation of imatinib-resistant CML cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;21(4):833-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3317. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25501124
-
ASP210: a potent oligonucleotide-based inhibitor effective against TKI-resistant CML cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):C184-C192. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00188.2024. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38826137 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitor targeting the Hsp70-Bim protein-protein interaction in CML cells overcomes BCR-ABL-independent TKI resistance.Leukemia. 2021 Oct;35(10):2862-2874. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01283-5. Epub 2021 May 18. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 34007045
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to ABL Kinase Inhibition in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and the Development of Next Generation ABL Kinase Inhibitors.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017 Aug;31(4):589-612. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2017.04.007. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28673390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Bcr-Abl inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia: keeping resistance in check.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):865-78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.865. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491988 Review.
Cited by
-
HSP90 inhibition without heat shock response.Blood. 2018 Jul 19;132(3):241-242. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-850271. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30026301 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Model of the ETR1 Ethylene Receptor Transmembrane Sensor Domain.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 20;9(1):8869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45189-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31222090 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Protein 90 Triggers Multi-Drug Resistance of Ovarian Cancer via AKT/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 2;11:620907. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.620907. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33738259 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy Resistance and Disease Progression in CML: Mechanistic Links and Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2022 Dec;17(6):181-197. doi: 10.1007/s11899-022-00679-z. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2022. PMID: 36258106 Review.
-
BCR: a promiscuous fusion partner in hematopoietic disorders.Oncotarget. 2019 Apr 12;10(28):2738-2754. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26837. eCollection 2019 Apr 12. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31105873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamaki H, Nakajima M, Shimotohno KW, Tanaka N. Molecular basis for the actions of Hsp90 inhibitors and cancer therapy. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2011;64(9):635-644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

