HCC-derived exosomes elicit HCC progression and recurrence by epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway
- PMID: 29725020
- PMCID: PMC5938707
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0534-9
HCC-derived exosomes elicit HCC progression and recurrence by epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway
Abstract
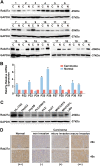
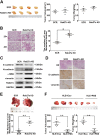
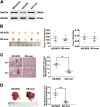
Liver cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Approximately 70-90% of primary liver cancers are hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Currently, HCC patient prognosis is unsatisfactory due to high metastasis and/or post-surgical recurrence rates. Therefore, new therapeutic methods for inhibiting metastasis and recurrence are urgently needed. Exosomes are small lipid-bilayer vesicles that are implicated in tumour development and metastasis. Rab27a, a small GTPase, regulates exosome secretion by mediating multivesicular endosome docking at the plasma membrane. However, whether Rab27a participates in HCC cell-derived exosome exocytosis is unclear. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) frequently initiates metastasis. The role of HCC cell-derived exosomes in EMT remains unknown. We found that exosomes from highly metastatic MHCC97H cells could communicate with low metastatic HCC cells, increasing their migration, chemotaxis and invasion. Rab27a knockdown inhibited MHCC97H-derived exosome secretion, which consequently promoted migration, chemotaxis and invasion in parental MHCC97H cells. Mechanistic studies showed that the biological alterations in HCC cells treated with MHCC97H-derived exosomes or MHCC97H cells with reduced self-derived exosome secretion were caused by inducing EMT via MAPK/ERK signalling. Animal experiments indicated that exosome secretion blockade was associated with enhanced lung and intrahepatic metastasis of parental MHCC97H cells, while ectopic overexpression of Rab27a in MHCC97H cells could rescue this enhancement of metastasis in vivo. Injection of MHCC97H cell-derived exosomes through the tail vein promoted intrahepatic recurrence of HLE tumours in vivo. Clinically, Rab27a was positively associated with serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level, vascular invasion and liver cirrhosis. Our study elucidated the role of exosomes in HCC metastasis and recurrence, suggesting that they are promising therapeutic and prognostic targets for HCC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Torre LA, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

