Heterogeneity and specialized functions of translation machinery: from genes to organisms
- PMID: 29725087
- PMCID: PMC6813789
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-018-0008-z
Heterogeneity and specialized functions of translation machinery: from genes to organisms
Abstract
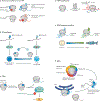
Regulation of mRNA translation offers the opportunity to diversify the expression and abundance of proteins made from individual gene products in cells, tissues and organisms. Emerging evidence has highlighted variation in the composition and activity of several large, highly conserved translation complexes as a means to differentially control gene expression. Heterogeneity and specialized functions of individual components of the ribosome and of the translation initiation factor complexes eIF3 and eIF4F, which are required for recruitment of the ribosome to the mRNA 5' untranslated region, have been identified. In this Review, we summarize the evidence for selective mRNA translation by components of these macromolecular complexes as a means to dynamically control the translation of the proteome in time and space. We further discuss the implications of this form of gene expression regulation for a growing number of human genetic disorders associated with mutations in the translation machinery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

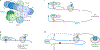
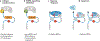

References
-
- Kong J & Lasko P Translational control in cellular and developmental processes. Nat. Rev. Genet 13, 383–394 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Curtis D, Lehmann R & Zamore P Translational regulation in development. Cell 81, 171–178 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Schwanhausser B et al. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473, 337–342 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Beyer A & Aebersold R On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell 165, 535–550 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

