Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation evokes resonant neural activity
- PMID: 29727475
- PMCID: PMC6025792
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25234
Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation evokes resonant neural activity
Abstract
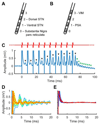
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a rapidly expanding treatment for neurological and psychiatric conditions; however, a target-specific biomarker is required to optimize therapy. Here, we show that DBS evokes a large-amplitude resonant neural response focally in the subthalamic nucleus. This response is greatest in the dorsal region (the clinically optimal stimulation target for Parkinson disease), coincides with improved clinical performance, is chronically recordable, and is present under general anesthesia. These features make it a readily utilizable electrophysiological signal that could potentially be used for guiding electrode implantation surgery and tailoring DBS therapy to improve patient outcomes. Ann Neurol 2018;83:1027-1031.
© 2018 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
Figures

References
-
- Montgomery EB., Jr . Deep brain stimulation programming: mechanisms, principles, and practice. Oxford, UK: University Press; 2016.
-
- Denys D, Feenstra M, Schuurman R. Deep brain stimulation: a new frontier in psychiatry. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Science + Business Media; 2012.
-
- McDermott H. Neurobionics: the biomedical engineering of neural prostheses. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2016. Neurobionics: treatments for disorders of the central nervous system; pp. 213–230.
-
- Pereira EA, Green AL, Nandi D, Aziz TZ. Deep brain stimulation: indications and evidence. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2007;4:591–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

