Neuropilin-1 promotes the oncogenic Tenascin-C/integrin β3 pathway and modulates chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29728077
- PMCID: PMC5935908
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4446-y
Neuropilin-1 promotes the oncogenic Tenascin-C/integrin β3 pathway and modulates chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), a non-tyrosine kinase glycoprotein receptor, is associated with poor prognosis breast cancer, however transcriptomic changes triggered by NRP-1 overexpression and its association with chemoresistance in breast cancer have not yet been explored.
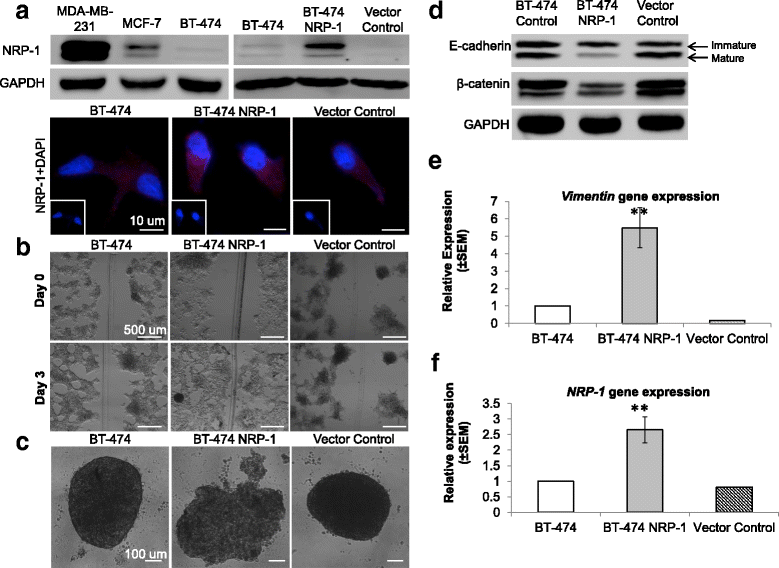
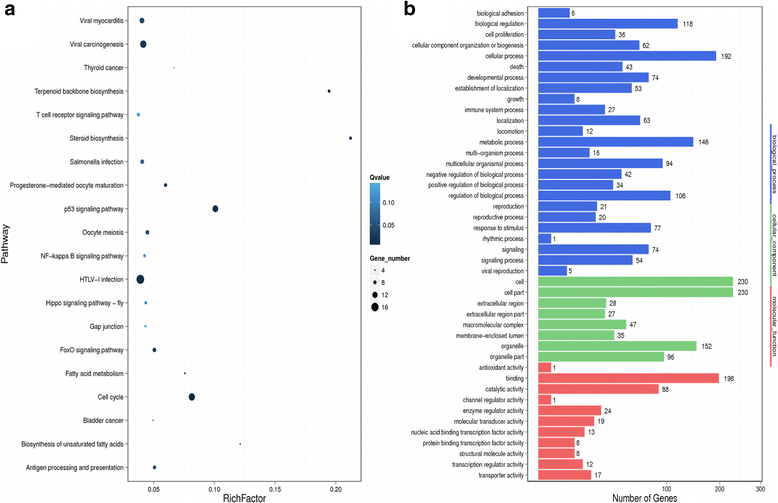
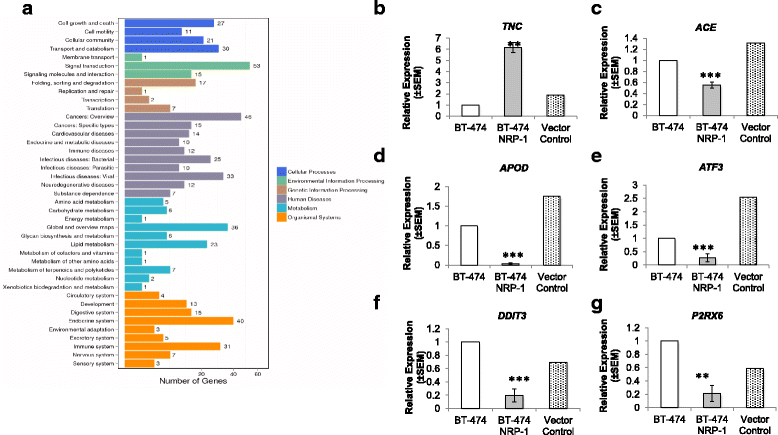
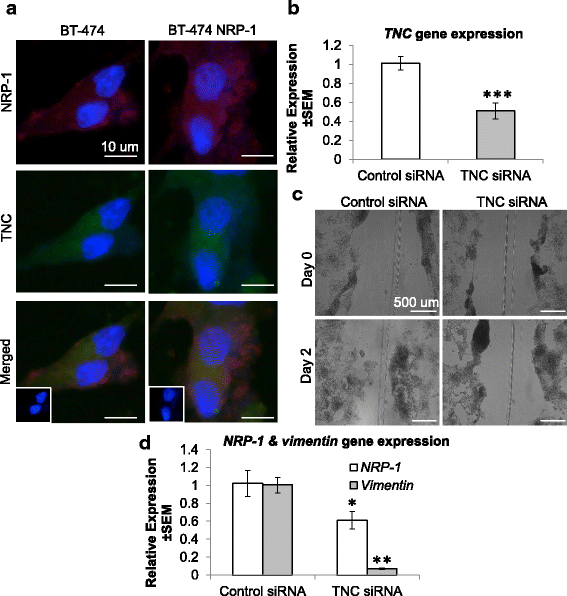
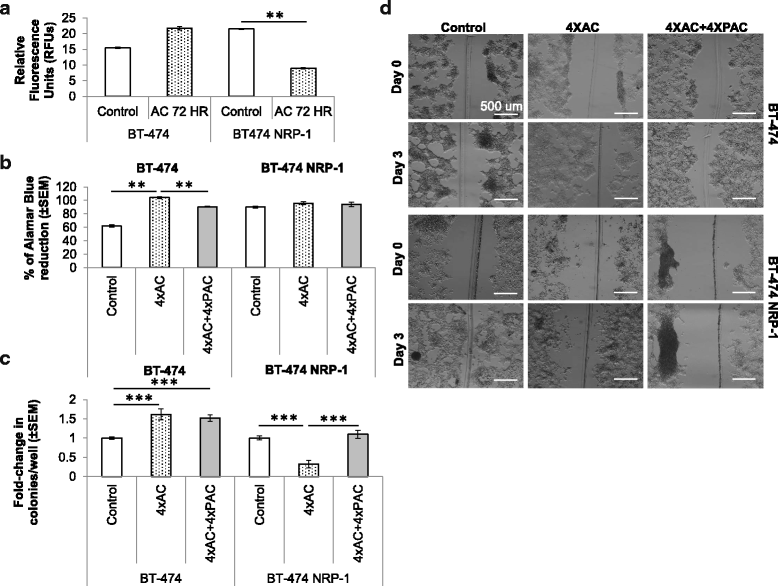
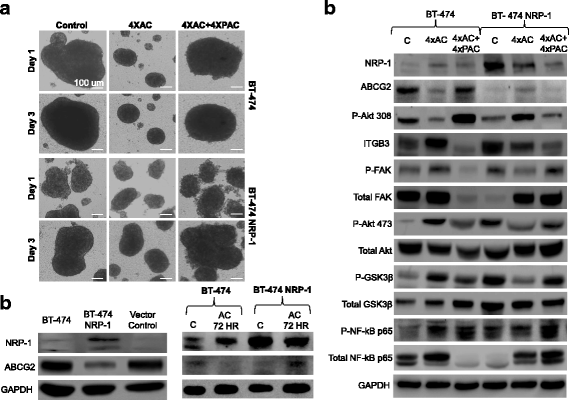
Methods: BT-474 NRP-1 variant cells were generated by stable overexpression of NRP-1 in the BT-474 breast cancer cell line. RNA sequencing and qRT-PCR were conducted to identify differentially expressed genes. The role of an upregulated oncogene, Tenascin C (TNC) and its associated pathway was investigated by siRNA-mediated knockdown. Resistant variants of the control and BT-474 NRP-1 cells were generated by sequential treatment with four cycles of Adriamycin/Cyclophosphamide (4xAC) followed by four cycles of Paclitaxel (4xAC + 4xPAC).
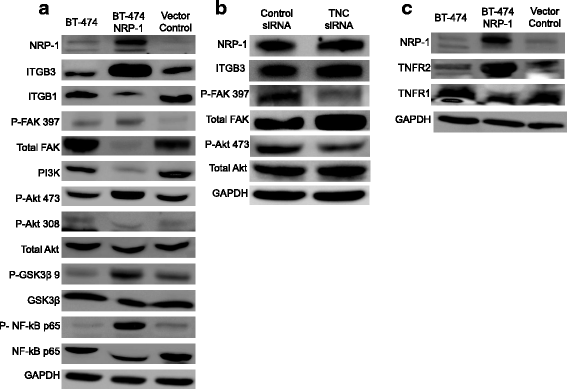
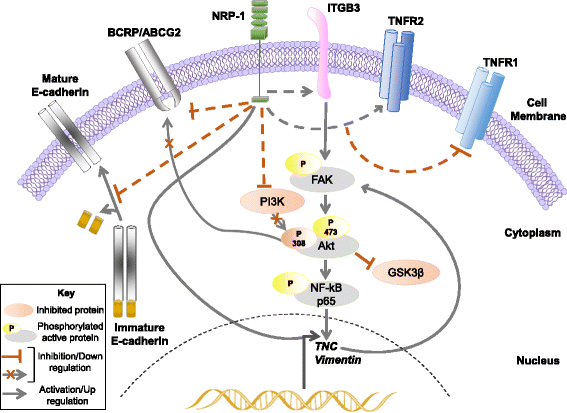
Results: NRP-1 overexpression increased cellular tumorigenic behavior. RNA sequencing identified upregulation of an oncogene, Tenascin-C (TNC) and downregulation of several tumor suppressors in BT-474 NRP-1 cells. Additionally, protein analysis indicated activation of the TNC-associated integrin β3 (ITGB3) pathway via focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Akt (Ser473) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) p65. siRNA-mediated TNC knockdown ablated the migratory capacity of BT-474 NRP-1 cells and inactivated FAK/Akt473 signaling. NRP-1 overexpressing cells downregulated breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Consequently, sequential treatment with Adriamycin/Cyclophosphamide (AC) cytotoxic drugs to generate resistant cells indicated that BT-474 NRP-1 cells increased sensitivity to treatment by inactivating NRP-1/ITGB3/FAK/Akt/NF-kB p65 signaling compared to wild-type BT-474 resistant cells.
Conclusions: We thus report a novel mechanism correlating high baseline NRP-1 with upregulated TNC/ITGB3 signaling, but decreased ABCG2 expression, which sensitizes BT-474 NRP-1 cells to Adriamycin/Cyclophosphamide. The study emphasizes on the targetability of the NRP-1/ITGB3 axis and its potential as a predictive biomarker for chemotherapy response.
Keywords: ABCG2; Adriamycin; Breast cancer; Chemoresistance; Cyclophosphamide; Integrin beta 3; NRP-1; TNC.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Adham SA, Al Harrasi I, Al Haddabi I, Al Rashdi A, Al Sinawi S, Al Maniri A, Ba-Omar T, Coomber BL. Immunohistological insight into the correlation between neuropilin-1 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014;62(9):619–631. doi: 10.1369/0022155414538821. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Naik A, Al-Zeheimi N, Bakheit CS, Al Riyami M, Al Jarrah A, Al Moundhri MS, Al Habsi Z, Basheer M, Adham SA. Neuropilin-1 associated molecules in the blood distinguish poor prognosis breast Cancer: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3301. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03280-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

