Neonatal Growth Restriction Slows Cardiomyocyte Development and Reduces Adult Heart Size
- PMID: 29729218
- PMCID: PMC6218323
- DOI: 10.1002/ar.23851
Neonatal Growth Restriction Slows Cardiomyocyte Development and Reduces Adult Heart Size
Abstract
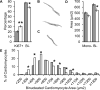
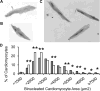
Prematurity is associated with reduced cardiac dimensions and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. While prematurity is typically associated with ex utero neonatal growth restriction (GR), the independent effect of neonatal GR on cardiac development has not been established. We tested the hypothesis that isolated neonatal GR decreases cardiomyocyte growth and proliferation, leading to long-term alterations in cardiac morphology. C57BL/6 mice were fostered in litters ranging in size from 6 to 12 pups to accentuate normal variation in neonatal growth. Regardless of litter size, GR was defined by a weight below the 10th percentile. On postnatal day 8, Ki67 immunoreactivity, cardiomyocyte nucleation status and cardiomyocyte profile area were assessed. For adult mice, cardiomyocyte area was determined, along with cardiac dimensions by echocardiography and cardiac fibrosis by Masson's trichrome stain. On day 8, cardiomyocytes from GR versus control mice were significantly smaller and less likely to be binucleated with evidence of persistent cell cycle activity. As adults, GR mice continued to have smaller cardiomyocytes, as well as decreased left ventricular volumes without signs of fibrosis. Neonatal GR reduces cardiomyocyte size, delays the completion of binucleation, and leads to long-term alterations in cardiac morphology. Clinical studies are needed to ascertain whether these results translate to preterm infants that must continue to grow and mature in the midst of the increased circulatory demands that accompany their premature transition to an ex utero existence. Anat Rec, 2018. © 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: cardiac development; cardiomyocyte; growth; left ventricle; prematurity.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Bai S, Campbell SE, Moore JA, Morales MC, Gerdes AM. Influence of age, growth, and sex on cardiac myocyte size and number in rats. Anat Rec. 1990;226:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee I, Fuseler JW, Price RL, Borg TK, Baudino TA. Determination of cell types and numbers during cardiac development in the neonatal and adult rat and mouse. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293:H1883–H1891. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Winter PD, Osmond C, Margetts B, Simmonds SJ. Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1989;2:577–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

