Identification of Near-Pan-neutralizing Antibodies against HIV-1 by Deconvolution of Plasma Humoral Responses
- PMID: 29731169
- PMCID: PMC6003858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.061
Identification of Near-Pan-neutralizing Antibodies against HIV-1 by Deconvolution of Plasma Humoral Responses
Abstract
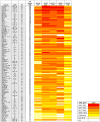
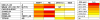
Anti-HIV-1 envelope broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (bNAbs) isolated from memory B cells may not fully represent HIV-1-neutralizing profiles measured in plasma. Accordingly, we characterized near-pan-neutralizing antibodies extracted directly from the plasma of two "elite neutralizers." Circulating anti-gp120 polyclonal antibodies were deconvoluted using proteomics to guide lineage analysis of bone marrow plasma cells. In both subjects, a single lineage of anti-CD4-binding site (CD4bs) antibodies explained the plasma-neutralizing activity. Importantly, members of these lineages potently neutralized 89%-100% of a multi-tier 117 pseudovirus panel, closely matching the specificity and breadth of the circulating antibodies. X-ray crystallographic analysis of one monoclonal, N49P7, suggested a unique ability to bypass the CD4bs Phe43 cavity, while reaching deep into highly conserved residues of Layer 3 of the gp120 inner domain, likely explaining its extreme potency and breadth. Further direct analyses of plasma anti-HIV-1 bNAbs should provide new insights for developing antibody-based antiviral agents and vaccines.
Keywords: HIV-1; antibody; broadly neutralizing antibody; humoral immunity; pan-neutralization; repertoire.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Brunger AT. Free R value: Cross-validation in crystallography. Method Enzymol. 1997;277:366–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

