Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy and in Combination with Ipilimumab in Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 29731394
- PMCID: PMC6750707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.001
Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy and in Combination with Ipilimumab in Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Erratum in
-
Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy and in Combination with Ipilimumab in Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2019 Feb 11;35(2):329. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.011. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30753829 No abstract available.
Abstract
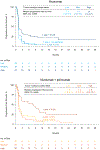
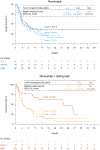
Durable responses and encouraging survival have been demonstrated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), but predictive markers are unknown. We used whole exome sequencing to evaluate the impact of tumor mutational burden on efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy or combined with ipilimumab in patients with SCLC from the nonrandomized or randomized cohorts of CheckMate 032. Patients received nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks) or nivolumab plus ipilimumab (1 mg/kg plus 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four cycles, followed by nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks). Efficacy of nivolumab ± ipilimumab was enhanced in patients with high tumor mutational burden. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab appeared to provide a greater clinical benefit than nivolumab monotherapy in the high tumor mutational burden tertile.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD-1; biomarkers; clinical trial; immunotherapy; ipilimumab; nivolumab; small cell lung cancer; tumor mutation burden.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Matthew D. Hellmann reports paid consultancy from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Merck, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Shattuck Labs, research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, and patent filed by Memorial Sloan Kettering related to the use of tumor mutation burden to predict response to immunotherapy (PCT/US2015/062208); Margaret K. Callahan reports grants from and employment of a family member by Bristol-Myers Squibb; personal fees for advisory board participation from AstraZeneca and Incyte; Mark M. Awad reports consulting or advisory role for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Merck, and Pfizer; Paolo A. Ascierto reports grants for research funding and personal fees for advisory/consultant role from Array, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche-Genentech, and personal fees for advisory/consultant role from Amgen, Genmab, Incyte, Medimmune, Merck Serono, NewLink Genetics, Novartis, and Pierre Fabre; Akin Atmaca reports travel grants and honoraria for advisory board participation from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Roche; Naiyer A. Rizvi reports a leadership role with ARMO Biosciences, stock or other ownership from ARMO Biosciences and Gritstone Oncology, consulting or advisory role for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Genentech, MedImmune, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; Giovanni Selvaggi reports employment by Bristol-Myers Squibb; Joseph D. Szustakowski reports employment and stock ownership from Bristol-Myers Squibb and previous employment and stock ownership from Novartis; Ariella Sasson reports employment by Bristol-Myers Squibb; Ryan Golhar reports employment by Bristol-Myers Squibb; Patrik Vitazka reports employment by Bristol-Myers Squibb; Han Chang reports employment by Bristol-Myers Squibb; William J. Geese reports employment and stock ownership from Bristol-Myers Squibb; Scott J. Antonia reports stock or other ownership from Cellular Biomedicine Group, and honoraria, consulting or advisory role, travel, accommodations, and expenses from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Merck; all other authors report nothing to disclose.
Figures

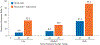

Comment in
-
Genomic Features of Response to Combination Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2018 May 14;33(5):791-793. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.005. Cancer Cell. 2018. PMID: 29763618
-
Tumor mutational burden (TMB) as a biomarker of response to immunotherapy in small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Aug;10(8):4689-4693. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.07.120. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30233840 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jäger D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F, et al. (2016). Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. The Lancet. Oncology 17, 883–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

