Comparative evaluation of toric intraocular lens alignment and visual quality with image-guided surgery and conventional three-step manual marking
- PMID: 29731603
- PMCID: PMC5923224
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S164175
Comparative evaluation of toric intraocular lens alignment and visual quality with image-guided surgery and conventional three-step manual marking
Abstract
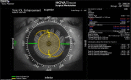
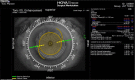
Purpose: To compare toric intraocular lens (IOL) alignment assisted by image-guided surgery or manual marking methods and its impact on visual quality.
Patients and methods: This prospective comparative study enrolled 80 eyes with cataract and astigmatism ≥1.5 D to undergo phacoemulsification with toric IOL alignment by manual marking method using bubble marker (group I, n=40) or Callisto eye and Z align (group II, n=40). Postoperatively, accuracy of alignment and visual quality was assessed with a ray tracing aberrometer. Primary outcome measure was deviation from the target axis of implantation. Secondary outcome measures were visual quality and acuity. Follow-up was performed on postoperative days (PODs) 1 and 30.
Results: Deviation from the target axis of implantation was significantly less in group II on PODs 1 and 30 (group I: 5.5°±3.3°, group II: 3.6°±2.6°; p=0.005). Postoperative refractive cylinder was -0.89±0.35 D in group I and -0.64±0.36 D in group II (p=0.003). Visual acuity was comparable between both the groups. Visual quality measured in terms of Strehl ratio (p<0.05) and modulation transfer function (MTF) (p<0.05) was significantly better in the image-guided surgery group. Significant negative correlation was observed between deviation from target axis and visual quality parameters (Strehl ratio and MTF) (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Image-guided surgery allows precise alignment of toric IOL without need for reference marking. It is associated with superior visual quality which correlates with the precision of IOL alignment.
Keywords: Callisto eye and Z align toric IOL; image-guided surgery; manual marking toric IOL; toric IOL alignment; visual quality image-guided surgery; visual quality toric IOL.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffmann PC, Hütz WW. Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for corneal astigmatism in 23,239 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:1479–1485. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, González-Méijome JM, Cerviño A. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:70–75. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correcting astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994;20:523–526. - PubMed
-
- Felipe A, Artigas JM, Díez-Ajenjo A, García-Domene C, Alcocer P. Residual astigmatism produced by toric intraocular lens rotation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:1895–1901. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

