Therapeutic effects of pegylated-interferon-α2a in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 29731688
- PMCID: PMC5927168
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2018.74868
Therapeutic effects of pegylated-interferon-α2a in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS). EAE is mainly mediated by adaptive and innate immune responses that lead to an inflammatory demyelination and axonal damage. The aim of the present research was to examine the therapeutic efficacy of Peg interferon alpha 2a (Peg-IFN α-2a) as a serine protease inhibitor on EAE model.
Material and methods: EAE induction was performed in female C57BL/6 mice by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (35-55) (MOG35-55) in Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) emulsion, and Peg-IFN α-2a was used for the treatment of EAE. During the course of the study, clinical evaluation was assessed, and on day 21 post-immunisation blood samples were taken from the heart of mice for evaluation of IL-6, and enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants. The mice were sacrificed and the brains and cerebellums were removed for histological analysis.
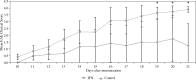
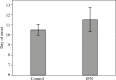
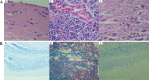
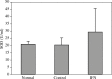
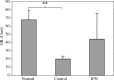
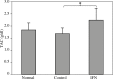
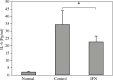
Results: Our findings indicated that Peg-IFN α-2a had beneficial effects on EAE by attenuation of the severity and a delay in the onset of disease. Histological analysis showed that treatment with Peg-IFN α-2a can reduce inflammation criteria. Moreover, in Peg-IFN α-2a-treated mice the serum level of IL-6 was significantly less than in controls, and total antioxidant capacity was significantly more than in the control animals.
Conclusions: These data indicate that Peg-IFN α-2a as an anti-serine protease with immunomodulatory properties may be useful for the treatment of MS.
Keywords: Peg interferon alpha 2a; antioxidant; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2001;50:121–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
