Interleukin-6 levels in the serum and saliva of patients with oral lichen planus compared with healthy controls: a meta-analysis study
- PMID: 29731693
- PMCID: PMC5927179
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2018.74880
Interleukin-6 levels in the serum and saliva of patients with oral lichen planus compared with healthy controls: a meta-analysis study
Abstract
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine that contributes to the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus (OLP). The aim of this meta-analysis study is the evaluation of IL-6 levels in the serum and saliva of patients with OLP compared with healthy controls. We searched the studies in 5 databases: PubMed/Medline, Scopus, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, from 1983 to Oct 31, 2016. Eleven studies were analysed for the meta-analysis study. The reviewers independently evaluated the quality of each included study using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS). A random-effects meta-analysis, using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 2.0, was used to reflect the variation in studies. Heterogeneity between estimates was evaluated by the Q and I2 statistics and for the Q statistic; heterogeneity was considered for p < 0.1. Eleven studies included 529 OLP patients and 333 healthy controls. The review identified two different biomaterials used for IL-6 assays: saliva and serum. The mean quality score of eleven studies was 7 (high quality). Estimates pooled from 6 studies showed significant high saliva IL-6 levels in OLP patients compared with healthy controls (the standardised difference in means (SDM) = 4.534, 95% CI = 1.915-7.153, p = 0.001). Also, estimates pooled from 7 studies showed significantly high serum IL-6 levels in OLP patients compared with healthy controls (SDM = 1.482, 95% CI = 0.524-2.439, p = 0.002). The higher levels of IL-6 in saliva compared with serum suggest that measurement of this marker in saliva may be more useful than serum for diagnostic and therapeutic aims.
Keywords: interleukin-6; lichen planus; saliva; serum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
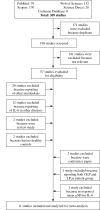



References
-
- Abdel-Haq A, Kusnierz-Cabala B, Darczuk D, et al. Interleukin-6 and neopterin levels in the serum and saliva of patients with Lichen planus and oral Lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 2014;43:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Gu GM, Martin MD, Darveau RP, et al. Oral and serum IL-6 levels in oral lichen planus patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98:673–678. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffari HR, Rahmani M, Rezaei F, et al. Evaluation of oral lichen planus frequency in patients referred to pathology centers of Kermanshah city, during 2008 to 2011. Sch J App Med Sci. 2016;4:2200–2202.
-
- Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ, et al. The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:350–365. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
