Macrophage Lamin A/C Regulates Inflammation and the Development of Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 29731750
- PMCID: PMC5920030
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00696
Macrophage Lamin A/C Regulates Inflammation and the Development of Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance
Abstract
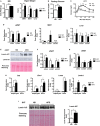
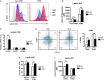
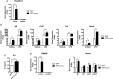
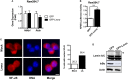
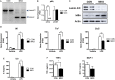
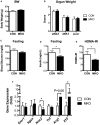
Obesity-induced chronic low-grade inflammation, in particular in adipose tissue, contributes to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. However, the mechanism by which obesity induces adipose tissue inflammation has not been completely elucidated. Recent studies suggest that alteration of the nuclear lamina is associated with age-associated chronic inflammation in humans and fly. These findings led us to investigate whether the nuclear lamina regulates obesity-mediated chronic inflammation. In this study, we show that lamin A/C mediates inflammation in macrophages. The gene and protein expression levels of lamin A/C are significantly increased in epididymal adipose tissues from obese rodent models and omental fat from obese human subjects compared to their lean controls. Flow cytometry and gene expression analyses reveal that the protein and gene expression levels of lamin A/C are increased in adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs) by obesity. We further show that ectopic overexpression of lamin A/C in macrophages spontaneously activates NF-κB, and increases the gene expression levels of proinflammatory genes, such as Il6, Tnf, Ccl2, and Nos2. Conversely, deletion of lamin A/C in macrophages reduces LPS-induced expression of these proinflammatory genes. Importantly, we find that myeloid cell-specific lamin A/C deficiency ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation. Thus, our data suggest that lamin A/C mediates the activation of ATM inflammation by regulating NF-κB, thereby contributing to the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance.
Keywords: adipose tissue; inflammation; insulin resistance; lamin A/C; macrophages; obesity.
Figures
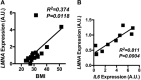
Similar articles
-
Clcn3 deficiency ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity and adipose tissue macrophage inflammation in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Dec;40(12):1532-1543. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0229-5. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31165783 Free PMC article.
-
FNDC5 attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization in obesity.Metabolism. 2018 Jun;83:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.01.013. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Metabolism. 2018. PMID: 29374559
-
Unique metabolic activation of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity promotes inflammatory responses.Diabetologia. 2018 Apr;61(4):942-953. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4526-6. Epub 2018 Jan 14. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29333574 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose tissue macrophage heterogeneity in the single-cell genomics era.Mol Cells. 2024 Feb;47(2):100031. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100031. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 38354858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose tissue macrophages: going off track during obesity.Diabetologia. 2016 May;59(5):879-94. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3904-9. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26940592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 27;13(9):2568. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092568. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731097 Free PMC article.
-
Lamin A/C: Function in Normal and Tumor Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;12(12):3688. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123688. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33316938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Native lamin A/C proteomes and novel partners from heart and skeletal muscle in a mouse chronic inflammation model of human frailty.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 23;11:1240285. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1240285. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37936983 Free PMC article.
-
Plants as Sources of Anti-Inflammatory Agents.Molecules. 2020 Aug 15;25(16):3726. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163726. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32824133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of biomarkers, pathways and potential therapeutic agents for white adipocyte insulin resistance using bioinformatics analysis.Adipocyte. 2019 Dec;8(1):318-329. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2019.1649578. Adipocyte. 2019. PMID: 31407623 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

