Overexpression of MMP21 and MMP28 is associated with gastric cancer progression and poor prognosis
- PMID: 29731903
- PMCID: PMC5920775
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8328
Overexpression of MMP21 and MMP28 is associated with gastric cancer progression and poor prognosis
Abstract
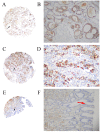
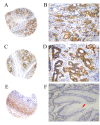
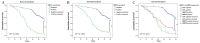
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-21 and MMP-28, or epilysin, are overexpressed during the invasion and metastasis of solid tumors. The present study investigated MMP-21 and MMP-28 expression levels in human gastric cancer using tissue microarray (TMA) analysis, and determined their association with clinicopathological characteristics and patient prognosis. TMA blocks, including 436 cases of gastric cancer and 92 non-cancerous adjacent gastric tissues, were investigated using immunohistochemistry. Staining results were analyzed statistically in association with various clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival. The MMP-21 and MMP-28 positive detection rate was 31.9% (139/436) and 34.4% (150/436), respectively, in the gastric carcinoma tissue specimens. MMP-21 and MMP-28 expression levels were negative in the 92 normal gastric tissue samples. In patients with gastric cancer, positive expression of MMP-21 and MMP-28 was correlated with tumor diameter, depth of invasion, vessel invasion, lymph node and distant metastases and tumor-node-metastasis stage. The overall survival rate was significantly lower in MMP-21 and MMP-28-positive compared with negative patients. Cox multivariate analysis revealed that MMP-21 and MMP-28 levels were independent predictors of survival in patients with gastric cancer. These findings emphasize the importance of MMP-21 and MMP-28, which may serve as novel and independent prognostic markers for the invasion and metastasis of human gastric cancer.
Keywords: cancer progression; gastric cancer; matrix metalloproteinase-21; matrix metalloproteinase-28; prognosis; tissue microarray.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imbalance between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in invasiveness and metastasis of human gastric carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 May;9(5):899-904. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.899. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12717827 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is associated with disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with gastric cancer.Int J Cancer. 2011 Aug 15;129(4):887-95. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25734. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20957628
-
Overexpression of twist and matrix metalloproteinase-9 with metastasis and prognosis in gastric cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5055-60. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.9.5055. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24175775
-
Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-21 is associated with poor overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer.J Gastrointest Surg. 2011 Jul;15(7):1188-94. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1519-5. Epub 2011 May 18. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011. PMID: 21590459
-
Overexpression of forkhead box M1 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator in gastric cancer is associated with cancer progression and poor prognosis.Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):7288-7296. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7136. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29344165 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of senescence genes in the treatment, prognosis, and tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):6926-6938. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38187003 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt activation disturbs cell competition and causes diffuse invasion of transformed cells through NF-κB-MMP21 pathway.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 3;14(1):7048. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42774-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37923722 Free PMC article.
-
Lethal toxicity of metformin on zebrafish during early embryonic development by multi-omics analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 2;15(1):11309. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95816-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175592 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Clinical Significance of MMP-28 in Bladder Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820974017. doi: 10.1177/1533033820974017. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33191847 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM17 promotes the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via upregulation MMP21.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Oct 21;20:516. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01556-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33100908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yabusaki H, Nashimoto A, Matsuki A, Aizawa M. Significance of surgical treatment in multimodal therapy for stage IV highly advanced gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60:377–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
