Peritumoral overexpression of ZBP-89 is associated with unfavorable disease-free survival rates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy
- PMID: 29731904
- PMCID: PMC5920541
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8353
Peritumoral overexpression of ZBP-89 is associated with unfavorable disease-free survival rates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy
Abstract
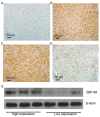
Previous studies have revealed that the peritumoral environment has a profound influence on tumor initiation and progression. Zinc-binding protein-89 (ZBP-89) has been observed to be involved with tumor development, recurrence, and metastasis. High intratumoral expression of ZBP-89 has been associated with improved prognosis in several tumor types. However, the prognostic values of peritumoral expression of ZBP-89 remain to be elucidated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) following curative resection. In the present study, peritumoral ZBP-89 expression was examined using immunohistochemistry in 102 HCC patients who had received curative hepatectomy. Expression of ZBP-89 protein was positive in 66.3% of the peritumoral samples from 102 HCC patients. HCC patients with high peritumoral ZBP-89 expression exhibited significantly shorter disease-free survival (DFS) times (P=0.012) than those patients with low peritumoral ZBP-89 expression. Additionally, high ZBP-89 expression in peritumoral HCC tissue was positively associated with the presence of liver cirrhosis. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analyses demonstrated that albumin levels ≤35 g/l, multiple tumors, tumor sizes ≥5 cm, and macroscopic vascular invasion may serve as independent prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) [hazard ratio (HR)=2.031; P=0.014] in patients with HCC. The multivariate Cox regression model identified that high ZBP-89 expression, multiple tumors and macroscopic vascular invasion were independent prognostic factors for shorter DFS durations. High expression of ZBP-89 in peritumoral HCC tissues was associated with a shorter DFS in HCC patients following curative hepatectomy. Additionally, high ZBP-89 expression in peritumoral HCC tissue was positively associated with the presence of liver cirrhosis in HCC patients, indicating that cirrhosis accompanied by high ZBP-89 expression may be a contributing factor to the poor prognosis of patients with HCC. Therefore, peritumoral ZBP-89 expression may be a good prognostic marker to predict DFS time in HCC patients following curative hepatectomy and may provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms of HCC initiation.
Keywords: ZBP-89; hepatocellular carcinoma; peritumoral; prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Positive Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 in Peritumoral Liver Tissue is Associated with Poor Survival after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2017 Aug;10(4):511-517. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 May 27. Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28558264 Free PMC article.
-
High-mobility group protein box1 expression correlates with peritumoral macrophage infiltration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 11;16(1):880. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2883-z. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27836008 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in peritumoral liver tissue is associated with poor survival after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jun 1;26(16):2707-16. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.6521. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18509183
-
Targeting ZBP-89 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Oct;22(10):817-822. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1516753. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 30142986 Review.
-
Advancing Hepatocellular Carcinoma Management Through Peritumoral Radiomics: Enhancing Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Nov 4;11:2159-2168. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S493227. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39525830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics model based on abdominal ultrasound for predicting Ki-67 expression in patients with hepatocellular cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 24;13:1209111. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1209111. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37711208 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based multiregional radiomics for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression in meningiomas: a two-center study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1554539. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1554539. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40777860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryerson AB, Eheman CR, Altekruse SF, Ward JW, Jemal A, Sherman RL, Henley SJ, Holtzman D, Lake A, Noone AM, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2012, featuring the increasing incidence of liver cancer. Cancer. 2016;122:1312–1337. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
