Treatment of a Patient with Merkel Cell Skin Carcinoma Using Radiation Therapy - A Case Report
- PMID: 29731938
- PMCID: PMC5927501
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.120
Treatment of a Patient with Merkel Cell Skin Carcinoma Using Radiation Therapy - A Case Report
Abstract
Background: Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare, very aggressive tumour. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but UV radiation, immunosuppression, and the presence of Merkel cell polyomavirus in the tumour genome appear to have a key role. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive tumour that often has a lethal end.
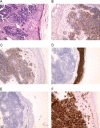
Cas report: A patient at 93 years of age comes for an examination by a dermatologist due to a rapidly growing nodular tumour growth in the forehead area. A tumour was about 3 cm in size. It had no signs of basal-cell carcinoma, no arborising vascularisation, no pigmentations on dermoscopy. Clinically, an eventual Merkel cell carcinoma was considered for the patient, but other primary skin tumours had to be excluded, as well as the possibility that regarding the patient's age, it may be a metastatic deposit. A skin biopsy was performed, as well as H-E examination and immunohistochemical analyses (positive CD56, positivity of neuroendocrine markers synaptophysin, chromogranin) which were in favour of Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin. After setting the diagnosis, our patient was treated with therapy which led to a complete withdrawal of a tumour. However, after 3 months the patient had repeated relapse of a tumour at the same site on the forehead and metastases in the retroauricular lymph nodes bilaterally. It shows that the radiotherapy as monotherapy has a great effect on the removal of the tumour formation, but unfortunately, it has no impact on lesion recurrence. It is also compatible with the literature data.
Conclusion: In many adult patients, as our case suggests, radiotherapy could be a good palliative treatment opportunity that should be considered, as well as a combination of radiation therapy with other oncologic therapeutic options.
Keywords: Carcinoma; Merkel cell; Radiotherapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Merkel cell carcinoma of the forehead area: a literature review and case report.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Sep;23(3):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s10006-019-00793-y. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31342210 Review.
-
Merkel Cell Carcinoma on the Face: Case Report.JMIR Dermatol. 2024 Apr 8;7:e56658. doi: 10.2196/56658. JMIR Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38512218 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel Cell Carcinoma of Unknown Primary Origin.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023 Dec;31(3):153-155. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023. PMID: 38439727
-
Differentiating Merkel cell carcinoma of lymph nodes without a detectable primary skin tumor from other metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas: The ELECTHIP criteria.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 May;78(5):964-972.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.037. Epub 2017 Nov 24. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29180096
-
[Recent update on tumour biology and treatment of Merkel Cell carcinoma].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2011 Dec;43(6):345-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1269932. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2011. PMID: 22241518 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Merkel cell carcinoma of the forehead area: a literature review and case report.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Sep;23(3):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s10006-019-00793-y. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31342210 Review.
References
-
- Llombart B, Requena C, Cruz J. Update on Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Epidemiology, Etiopathogenesis, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Staging. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:108–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2016.07.022. PMid:27770997. - PubMed
-
- Miles BA, Goldenberg D. Education Committee of the American Head and Neck Society (AHNS). Merkel cell carcinoma: Do you know your guidelines? Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2017;2017 - PubMed
-
- Zur Hausen A. Book of abstracts 47.VI Congress of dermatovenereologists of Macedonia with international participation. ISBN 978-9989-37-031-1.
-
- Becker JC, Stang A, Hausen AZ, Fischer N, DeCaprio JA, Tothill RW, Lyngaa R, Hansen UK, Ritter C, Nghiem P, Bichakjian CK, Ugurel S, Schrama D. Epidemiology, biology and therapy of Merkel cell carcinoma: conclusions from the EU project IMMOMEC. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017 PMid:29188306. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
