sEMG Signal Acquisition Strategy towards Hand FES Control
- PMID: 29732046
- PMCID: PMC5872608
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2350834
sEMG Signal Acquisition Strategy towards Hand FES Control
Abstract
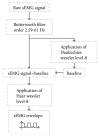
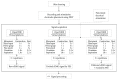
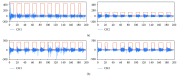
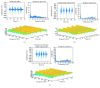
Due to damage of the nervous system, patients experience impediments in their daily life: severe fatigue, tremor or impaired hand dexterity, hemiparesis, or hemiplegia. Surface electromyography (sEMG) signal analysis is used to identify motion; however, standardization of electrode placement and classification of sEMG patterns are major challenges. This paper describes a technique used to acquire sEMG signals for five hand motion patterns from six able-bodied subjects using an array of recording and stimulation electrodes placed on the forearm and its effects over functional electrical stimulation (FES) and volitional sEMG combinations, in order to eventually control a sEMG-driven FES neuroprosthesis for upper limb rehabilitation. A two-part protocol was performed. First, personalized templates to place eight sEMG bipolar channels were designed; with these data, a universal template, called forearm electrode set (FELT), was built. Second, volitional and evoked movements were recorded during FES application. 95% classification accuracy was achieved using two sessions per movement. With the FELT, it was possible to perform FES and sEMG recordings simultaneously. Also, it was possible to extract the volitional and evoked sEMG from the raw signal, which is highly important for closed-loop FES control.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Stimulus Artifact Removal Technique for SEMG Signal Processing During Functional Electrical Stimulation.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015 Aug;62(8):1959-68. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2407834. Epub 2015 Feb 27. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 25730823
-
Evaluation of Hand Action Classification Performance Using Machine Learning Based on Signals from Two sEMG Electrodes.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;24(8):2383. doi: 10.3390/s24082383. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38676000 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid method for real-time stimulation artefact removal during functional electrical stimulation with time-variant parameters.J Neural Eng. 2021 Apr 26;18(4). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abf68c. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 33836509
-
Technology and instrumentation for detection and conditioning of the surface electromyographic signal: state of the art.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2009 Feb;24(2):122-34. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2008.08.006. Epub 2008 Nov 29. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2009. PMID: 19042063 Review.
-
Neurorehabilitation with new functional electrical stimulation for hemiparetic upper extremity in stroke patients.J Nippon Med Sch. 2008 Feb;75(1):4-14. doi: 10.1272/jnms.75.4. J Nippon Med Sch. 2008. PMID: 18360073 Review.
Cited by
-
Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of isotonic exercise monitoring device for measuring active knee extension.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 16;11:e14672. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14672. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36684676 Free PMC article.
-
Transformer-based hand gesture recognition from instantaneous to fused neural decomposition of high-density EMG signals.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 7;13(1):11000. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36490-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37419881 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Platform Implementation of an SSVEP-Based BCI for the Control of a 6-DOF Robotic Arm.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 2;22(13):5000. doi: 10.3390/s22135000. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808498 Free PMC article.
-
Embedded Bio-Mimetic System for Functional Electrical Stimulation Controlled by Event-Driven sEMG.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;20(5):1535. doi: 10.3390/s20051535. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamper D. G. Restoration of hand function in stroke and spinal cord injury. In: Reinkensmeyer D., Dietz V., editors. Neurorehabilitation Technology. 2nd. Cham: Springer; 2016. pp. 311–324. - DOI
-
- Altamirano A., Vera A., Muñoz R., Leija L., Wolf D. Multichannel sEMG signal analysis using Hilbert-Huang transform to identify time-frequency features. 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; August 2014; Chicago, IL, USA.
-
- Hou Y., Zurada J., Karwowski W. Prediction of EMG signals of trunk muscles in manual lifting using a neural network model. 2004. Proceedings. 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks; January 2004; Budapest, Hungary. pp. 1935–1940. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

