Type 2 Diabetes: When Does It Start?
- PMID: 29732459
- PMCID: PMC5932476
- DOI: 10.1210/js.2018-00071
Type 2 Diabetes: When Does It Start?
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to clarify the onset of diabetes.
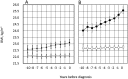
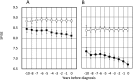
Design: Data from 27,392 nondiabetic health examinees were retrospectively analyzed for a mean of 5.3 years. Trajectories of fasting plasma glucose (FPG), body mass index (BMI), and the single point insulin sensitivity (Si) estimator (SPISE), an index of Si, 10 years before diagnosis of prediabetes (PDM; n = 4781) or diabetes (n = 1061) were separately assessed by a mixed effects model. Diabetes and PDM were diagnosed by the American Diabetes Association definition on the basis of FPG and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c values.
Results: In individuals who developed diabetes, mean FPG and BMI were significantly higher (P < 0.01 each) and SPISE lower than those who did not at -10 years: FPG 101.5 mg/dL vs 94.5 mg/dL, BMI 24.0 kg/m2 vs 22.7 kg/m2, and SPISE 7.32 vs 8.34, P < 0.01 each. These measurements, in subjects who developed prediabetes, were slightly but definitely different from those who did not, already at -10 years: FPG 91.8 mg/dL vs 89.6 mg/dL, BMI 22.6 kg/m2 vs 22.1 kg/m2, and SPISE 8.44 vs 8.82, P < 0.01 each. In both cases, the differences were progressively greater toward year 0, the time of diabetes, or PDM diagnosis.
Conclusions: FPG was significantly elevated in those who developed diabetes at least 10 years before diagnosis of diabetes, and this was also the case in those who developed PDM. Glucose dysregulation precedes diagnosis of diabetes at least for 20 years.
Keywords: Japanese; diabetes mellitus; prediabetes; starting point of diabetes; trajectory.
Figures

References
-
- Færch K, Witte DR, Tabák AG, Perreault L, Herder C, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M, Vistisen D. Trajectories of cardiometabolic risk factors before diagnosis of three subtypes of type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the longitudinal Whitehall II Cohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013;1(1):43–51. - PubMed
-
- Ferrannini E, Nannipieri M, Williams K, Gonzales C, Haffner SM, Stern MP. Mode of onset of type 2 diabetes from normal or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 2004;53(1):160–165. - PubMed
-
- Looker HC, Knowler WC, Hanson RL. Changes in BMI and weight before and after the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(11):1917–1922. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
