Salmonella Tol-Pal Reduces Outer Membrane Glycerophospholipid Levels for Envelope Homeostasis and Survival during Bacteremia
- PMID: 29735519
- PMCID: PMC6013679
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00173-18
Salmonella Tol-Pal Reduces Outer Membrane Glycerophospholipid Levels for Envelope Homeostasis and Survival during Bacteremia
Abstract
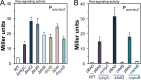
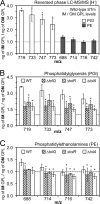
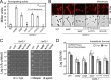
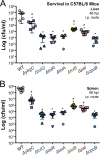
Salmonellae regulate membrane lipids during infection, but the exact proteins and mechanisms that promote their survival during bacteremia remain largely unknown. Mutations in genes encoding the conserved Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S Typhimurium) Tol-Pal apparatus caused the outer membrane (OM) sensor lipoprotein, RcsF, to become activated. The capsule activation phenotype for the mutants suggested that Tol-Pal might influence envelope lipid homeostasis. The mechanism involves reducing OM glycerophospholipid (GPL) levels, since the mutant salmonellae similarly accumulated phosphatidylglycerols (PGl) and phosphatidylethanolamines (PE) within the OM in comparison to the wild type. The data support the Escherichia coli model, whereby Tol-Pal directs retrograde GPL translocation across the periplasm. The S Typhimurium mechanism involves contributions from YbgC, a cytoplasmic acyl coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) thioesterase, and CpoB, a periplasmic TolA-binding protein. The functional relationship between Tol-Pal and YbgC and CpoB was previously unresolved. The S Typhimurium Tol-Pal proteins contribute similarly toward promoting OM-GPL homeostasis and Rcs signaling inactivity but differently toward promoting bacterial morphology, rifampin resistance, survival in macrophages, and survival in mice. For example, tolQ, tolR, tolA, and cpoB mutants were significantly more attenuated than ybgC, tolB, and pal mutants in a systemic mouse model of disease. Therefore, key roles exist for TolQ, TolR, TolA, and CpoB during murine bacteremia, which are independent of maintaining GPL homeostasis. The ability of TolQR to channel protons across the inner membrane (IM) is necessary for S Typhimurium TolQRA function, since mutating conserved channel-facing residues rendered TolQ ineffective at rescuing deletion mutant phenotypes. Therefore, Tol-Pal promotes S Typhimurium survival during bacteremia, in part, by reducing OM GPL concentrations, while TolQRA and CpoB enhance systemic virulence by additional mechanisms.
Keywords: CpoB/YbgF; Gram-negative bacteria; Intracellular; Pal; RcsF; Tol-Pal; TolA; TolB; TolQ; TolR; YbgC; anionic glycerophospholipids; bacteria; barrier; cell envelope; constriction; facultative; ion channel; lipid; lysosome; macrophage; membrane curvature; motor; mouse; outer membrane; pathogen; pathogenesis; peptidoglycan hydrolases; periplasm; phosphatidylethanolamines; phosphatidylglycerol; phospholipids; proton-motive force; salmonella; septation; systemic pathogenesis; trafficking; transenvelope complex; translocation; transport; vacuole; virulence.
Copyright © 2018 Masilamani et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Timing of TolA and TolQ Recruitment at the Septum Depends on the Functionality of the Tol-Pal System.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 15;434(7):167519. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167519. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35240126
-
Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Uses PbgA/YejM To Regulate Lipopolysaccharide Assembly during Bacteremia.Infect Immun. 2019 Dec 17;88(1):e00758-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00758-19. Print 2019 Dec 17. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31611279 Free PMC article.
-
The role of TolA, TolB, and TolR in cell morphology, OMVs production, and virulence of Salmonella Choleraesuis.AMB Express. 2022 Jan 25;12(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13568-022-01347-4. AMB Express. 2022. PMID: 35075554 Free PMC article.
-
Force-Generation by the Trans-Envelope Tol-Pal System.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 3;13:852176. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.852176. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35308353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tol proteins of Escherichia coli and their involvement in the uptake of biomolecules and outer membrane stability.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999 Aug 15;177(2):191-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13731.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10474183 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Activity Sensing in Bacteria in Regulating Metabolism and Motility.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 17;10:3055. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03055. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outer Membrane Vesicles of Gram-Negative Bacteria: An Outlook on Biogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 4;12:557902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.557902. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33746909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling through the Salmonella PbgA-LapB regulatory complex activates LpxC proteolysis and limits lipopolysaccharide biogenesis during stationary-phase growth.J Bacteriol. 2024 Apr 18;206(4):e0030823. doi: 10.1128/jb.00308-23. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38534107 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the Tol-Pal system in the Type III secretion system and flagella-mediated virulence in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 23;10(1):15173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72412-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32968151 Free PMC article.
-
The multifarious roles of Tol-Pal in Gram-negative bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020 Jul 1;44(4):490-506. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa018. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32472934 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

