Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Docking Studies of Novel Bisquaternary Aldoxime Reactivators on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibited by Paraoxon
- PMID: 29735900
- PMCID: PMC6100540
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051103
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Docking Studies of Novel Bisquaternary Aldoxime Reactivators on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibited by Paraoxon
Abstract
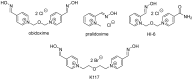
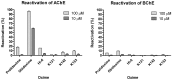
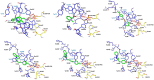
Nerve agents and oxon forms of organophosphorus pesticides act as strong irreversible inhibitors of two cholinesterases in the human body: acetylcholinesterase (AChE; EC 3.1.1.7) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; EC 3.1.1.8), and are therefore highly toxic compounds. For the recovery of inhibited AChE, antidotes from the group of pyridinium or bispyridinium aldoxime reactivators (pralidoxime, obidoxime, HI-6) are used in combination with anticholinergics and anticonvulsives. Therapeutic efficacy of reactivators (called “oximes”) depends on their chemical structure and also the type of organophosphorus inhibitor. Three novel oximes (K131, K142, K153) with an oxime group in position four of the pyridinium ring were designed and then tested for their potency to reactivate human (Homo sapiens sapiens) AChE (HssACHE) and BChE (HssBChE) inhibited by the pesticide paraoxon (diethyl 4-nitrophenyl phosphate). According to the obtained results, none of the prepared oximes were able to satisfactorily reactivate paraoxon-inhibited cholinesterases. On the contrary, extraordinary activity of obidoxime in the case of paraoxon-inhibited HssAChE reactivation was confirmed. Additional docking studies pointed to possible explanations for these results.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase; antidote; butyrylcholinesterase; organophosphate; oxime; paraoxon.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
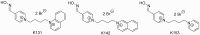
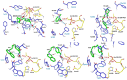
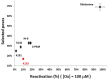
Similar articles
-
Potency of several oximes to reactivate human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibited by paraoxon in vitro.Chem Biol Interact. 2008 Sep 25;175(1-3):421-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 May 7. Chem Biol Interact. 2008. PMID: 18617161
-
In vitro ability of currently available oximes to reactivate organophosphate pesticide-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(3):2077-87. doi: 10.3390/ijms12032077. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21673941 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro oxime-assisted reactivation of paraoxon-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009 Jul;47(6):545-50. doi: 10.1080/15563650903058914. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19586353
-
Unequal efficacy of pyridinium oximes in acute organophosphate poisoning.Clin Med Res. 2007 Mar;5(1):71-82. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2007.701. Clin Med Res. 2007. PMID: 17456837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The development of new oximes and the evaluation of their reactivating, therapeutic and neuroprotective efficacy against tabun.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Oct;8(11):1134-43. doi: 10.2174/138955708785909871. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18855728 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Modeling and In Vitro Studies of a Neutral Oxime as a Potential Reactivator for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibited by Paraoxon.Molecules. 2018 Nov 12;23(11):2954. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112954. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30424582 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Group of AChE Reactivators-Synthesis, In Vitro Reactivation and Molecular Docking Study.Molecules. 2018 Sep 7;23(9):2291. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092291. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30205495 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Outcomes in Acute Organophosphate Poisoning With and Without N-acetyl Cysteine Intervention.Cureus. 2024 Jan 29;16(1):e53155. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53155. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38420067 Free PMC article.
-
Resurrection and Reactivation of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase.Chemistry. 2019 Apr 11;25(21):5337-5371. doi: 10.1002/chem.201805075. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Chemistry. 2019. PMID: 30444932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular modeling studies on the interactions of 7-methoxytacrine-4-pyridinealdoxime, 4-PA, 2-PAM, and obidoxime with VX-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase: a near attack conformation approach.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):1018-1029. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1609953. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31074292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carletti E., Aurbek N., Gillon E., Loiodice M., Nicolet Y., Fontecilla-Camps J.-C., Masson P., Thiermann H., Nachon F., Worek F. Structure-Activity Analysis of Aging and Reactivation of Human Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibited by Analogues of Tabun. Biochem. J. 2009;412:97–106. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090091. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Musilova L., Jun D., Kuca K., Pohanka M., Katalinic M., Kovarik Z. Development of New Antidotes of Organophosphate Intoxications: Oxime-Assisted Reactivation of Dimethoxy- and Diethoxy-Phosphorylated Human Butyrylcholinesterase for Construction of “pseudo Catalytic” Bioscavengers. Toxicol. Lett. 2009;189:S216. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.06.561. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

