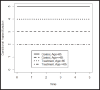
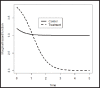
Simpson's Paradox: Examples
- PMID: 29736137
- PMCID: PMC5936043
- DOI: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.218026
Simpson's Paradox: Examples
Abstract
Simpson's paradox is very prevalent in many areas. It characterizes the inconsistency between the conditional and marginal interpretations of the data. In this paper, we illustrate through some examples how the Simpson's paradox can happen in continuous, categorical, and time-to-event data.
辛普森悖论普遍存在于很多领域。它具有数据 的条件性和边缘性解释之间的不一致特征。在本文中, 我们通过一些例子来阐述辛普森悖论是如何在连续性、 分类和时间- 事件数据中产生的。.
Keywords: conditional expectation; odd ratio; time-to-event analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Simpson EH. The Interpretation of Interaction in Contingency Tables. J R Stat Soc Series B. 1951; 13: 238-241
-
- Yule GU. Notes on the Theory of Association of Attributes in Statistics. Biometrika. 1903; 2(2): 121-134. doi: https:://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/2.2.121 - DOI
-
- Heydtmann M. The nature of truth: Simpson’s Paradox and the limits of statistical data. QJM. 2002; 95(4): 247-249. doi: https:://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/95.4.247 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lerman K. Computational social scientist beware: Simpson’s paradox in behavioral data. J Comput Soc Sc. 2018; 1: 49-58. doi: https:://doi.org/10.1007/s42001-017-0007-4 - DOI
-
- Malinas G, Bigelow J. Simpson’s Paradox. Edward N. Zalta. (ed.) The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2016 Edition). Available from: https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2016/entries/paradox-simpson
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources