The Effect of Perioperative Fluid Management on Intraocular Pressure during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Pelvic Surgery
- PMID: 29736280
- PMCID: PMC5874977
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1457851
The Effect of Perioperative Fluid Management on Intraocular Pressure during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Pelvic Surgery
Abstract
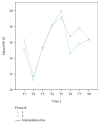
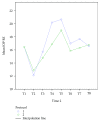
Purpose: Visual loss is a devastating perioperative complication that can result from elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). The Trendelenburg position during surgery increases IOP. The purpose of this study was to quantify IOP changes in patients undergoing laparoscopic hysterectomy, at different time points and body positions throughout the procedure, and to compare fluctuations of IOP during the perioperative period according to two fluid management protocols.
Methods: Thirty women scheduled to undergo elective gynecologic laparoscopic pelvic surgery were randomly allocated to receive a liberal or restrictive fluid management protocol. IOP, mean arterial pressure, heart rate, exhaled tidal volume, end-tidal CO2, and ocular perfusion pressure were assessed prior, during, and postsurgery, at 8 time points altogether.
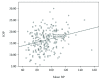
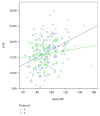
Results: Mean changes in IOP were similar for the two protocols; the peak IOP was at the steep (peak) Trendelenburg position. For each protocol, IOP correlated positively with mean arterial pressure, and mean blood pressure correlated with ocular perfusion pressure.
Conclusion: IOP was elevated during laparoscopic pelvic surgery and particularly at the steep Trendelenburg position. No differences were found in any of the parameters examined according to a liberal or restrictive fluid management protocol.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraocular pressure and steep Trendelenburg during minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: is there a risk?J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013 Nov-Dec;20(6):819-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013. PMID: 23941744
-
Does Restrictive Fluid Strategy during Robotic Pelvic Surgeries Obtund Intraoperative Rise in Intraocular Pressure?Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Jan-Mar;12(1):155-158. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_144_17. Anesth Essays Res. 2018. PMID: 29628573 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of steep trendelenburg positioning on intraocular pressure during robotic radical prostatectomy.Anesth Analg. 2009 Aug;109(2):473-8. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e3181a9098f. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19608821
-
The Impact of Steep Trendelenburg Position on Intraocular Pressure.J Clin Med. 2022 May 18;11(10):2844. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102844. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35628970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiology and Role of Intraocular Pressure in Contemporary Anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 2018 May;126(5):1551-1562. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002544. Anesth Analg. 2018. PMID: 29049074 Review.
Cited by
-
Complete Vision Loss after Laparoscopic Hysterectomy.Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb 28;2021:6643703. doi: 10.1155/2021/6643703. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33728078 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

