LMO4 mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29736306
- PMCID: PMC5934551
LMO4 mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer cells
Abstract
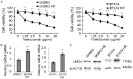
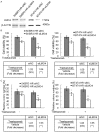
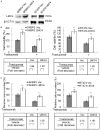
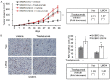
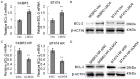
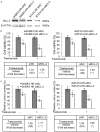
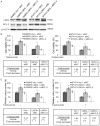
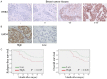
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women worldwide. Trastuzumab (Herceptin) is an effective antibody drug for HER2 positive breast cancer; de novo or acquired trastuzumab resistance retarded the use of trastuzumab for at least 70% of HER2 positive breast cancers. In this study, we reported LMO4 (a member of LIM-only proteins) promoted trastuzumab resistance in human breast cancer cells. Over-expression of LMO4 was observed in acquired trastuzumab resistance breast cancer cells SKBR3 HR and BT474 HR. Depletion of LMO4 partly abolished the trastuzumab resistance of SKBR3 HR and BT474 HR cells. Forced expression of LMO4 significantly increased trastuzumab resistance of HER2 positive breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. BCL-2 was regulated by LMO4 and mediated the promoting role of LMO4 in trastuzumab resistance of HER2 positive breast cancer cells. High level of LMO4 was associated with worse clinicopathological parameters (including tumor size and histological grade) and lower survival rate in HER2 positive breast cancer patients. LMO4 therefore could be used as a target to develop diagnostic and therapeutic methods for human HER2 positive breast cancer.
Keywords: BCL-2; HER2; LMO4; breast cancer; trastuzumab resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological blockade of fatty acid synthase (FASN) reverses acquired autoresistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin by transcriptionally inhibiting 'HER2 super-expression' occurring in high-dose trastuzumab-conditioned SKBR3/Tzb100 breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2007 Oct;31(4):769-76. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17786307
-
EGFR over-expression and activation in high HER2, ER negative breast cancer cell line induces trastuzumab resistance.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Aug;122(3):685-97. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0592-x. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 19859802
-
Erythropoietin receptor expression and its relationship with trastuzumab response and resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Dec;136(3):739-48. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2316-x. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 23117856
-
Therapeutic Strategies for Human Epidermal Receptor-2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2020 Aug 2;12(8):e9522. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9522. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32905036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Insights into the Development of Preclinical Trastuzumab- Resistant HER2+ Breast Cancer Models.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(17):1976-1998. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161216144659. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 27993109 Review.
Cited by
-
miR‑135b‑5p enhances the sensitivity of HER‑2 positive breast cancer to trastuzumab via binding to cyclin D2.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Oct;46(4):1514-1524. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4681. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32700749 Free PMC article.
-
Research and Clinical Significance of the Differentially Expressed Genes TP63 and LMO4 in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Related Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Am J Mens Health. 2021 Mar-Apr;15(2):15579883211011380. doi: 10.1177/15579883211011380. Am J Mens Health. 2021. PMID: 33906487 Free PMC article.
-
NR5A2 Is One of 12 Transcription Factors Predicting Prognosis in HNSCC and Regulates Cancer Cell Proliferation in a p53-Dependent Manner.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 1;11:691318. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.691318. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34277436 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 regulates LMO4 expression in psoriatic keratinocytes via AKT/STAT3 pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Dec;11(12):e1104. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1104. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38156380 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0058124 Aggravates the Progression of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by Activating LMO4 Expression via Targeting miR-370-3p.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Oct 1;12:9459-9470. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S271778. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33061633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polyak K, Metzger Filho O. SnapShot: breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:562–562.e1. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Yu X, Wang C, Pan S, Liang B, Zhang Y, Chong X, Meng Y, Dong J, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Wang H, Gao J, Wei H, Zhao J, Hu C, Xiao W, Li B. The anti-ErbB2 antibody H2-18 and the pan-PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 effectively inhibit trastuzumab-resistant ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:52877–52888. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korkaya H, Kim GI, Davis A, Malik F, Henry NL, Ithimakin S, Quraishi AA, Tawakkol N, D’Angelo R, Paulson AK, Chung S, Luther T, Paholak HJ, Liu SL, Hassan KA, Zen Q, Clouthier SG, Wicha MS. Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2+Breast cancer by expanding the cancer stem cell population. Molecular Cell. 2012;47:570–584. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
