Serum cytokine responses in Rickettsia felis infected febrile children, Ghana
- PMID: 29736763
- PMCID: PMC6096778
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-018-0544-3
Serum cytokine responses in Rickettsia felis infected febrile children, Ghana
Abstract
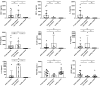
The intracellular pathogen Rickettsia felis causes flea-borne spotted fever and is increasingly recognized as an emerging cause of febrile illness in Africa, where co-infection with Plasmodium falciparum is common. Rickettsiae invade endothelial cells. Little is known, however, about the early immune responses to infection. In this study, we characterize for the first time the cytokine profile in the acute phase of illness caused by R. felis infection, as well as in plasmodial co-infection, using serum from 23 febrile children < 15 years of age and 20 age-matched healthy controls from Ghana. Levels of IL-8 (interleukin-8), IP-10 (interferon-γ-induced protein-10), MCP-1 (monocyte chemotactic protein-1), MIP-1α (macrophage inflammatory protein-1α) and VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) were significantly elevated in R. felis mono-infection; however, IL-8 and VEGF elevation was not observed in plasmodial co-infections. These results have important implications in understanding the early immune responses to R. felis and suggest a complex interplay in co-infections.
Keywords: Cytokine; Flea-borne spotted fever; Rickettsia felis; Rickettsiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest. No author has a commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest (e.g., pharmaceutical stock ownership, consultancy, advisory board membership, relevant patents, or research funding).
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

