Promoting Replicability in Developmental Research Through Meta-analyses: Insights From Language Acquisition Research
- PMID: 29736962
- PMCID: PMC6282795
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13079
Promoting Replicability in Developmental Research Through Meta-analyses: Insights From Language Acquisition Research
Abstract
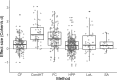
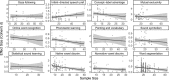
Previous work suggests that key factors for replicability, a necessary feature for theory building, include statistical power and appropriate research planning. These factors are examined by analyzing a collection of 12 standardized meta-analyses on language development between birth and 5 years. With a median effect size of Cohen's d = .45 and typical sample size of 18 participants, most research is underpowered (range = 6%-99%; median = 44%); and calculating power based on seminal publications is not a suitable strategy. Method choice can be improved, as shown in analyses on exclusion rates and effect size as a function of method. The article ends with a discussion on how to increase replicability in both language acquisition studies specifically and developmental research more generally.
© 2018 The Authors. Child Development published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychological Association . (2001). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Bergmann, C. , Tsuji, S. , & Cristia, A. (2017). Top‐down versus bottom‐up theories of phonological acquisition: A big data approach. Proceedings of Interspeech, 2017, 2013–2016. 10.21437/Interspeech.2017-1443 - DOI
-
- Black, A. , & Bergmann, C. (2017). Quantifying infants’ statistical word segmentation: A meta‐analysis In Gunzelmann G., Howes A., Tenbrink T., & Davelaar E. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 39th annual conference of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 124–129). Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

