Immunohistological features related to functional impairment in lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- PMID: 29739412
- PMCID: PMC5941479
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-018-0797-9
Immunohistological features related to functional impairment in lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Abstract
Background: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a low-grade neoplasm characterized by the pulmonary infiltration of smooth muscle-like cells (LAM cells) and cystic destruction. Patients usually present with airway obstruction in pulmonary function tests (PFTs). Previous studies have shown correlations among histological parameters, lung function abnormalities and prognosis in LAM. We investigated the lung tissue expression of proteins related to the mTOR pathway, angiogenesis and enzymatic activity and its correlation with functional parameters in LAM patients.
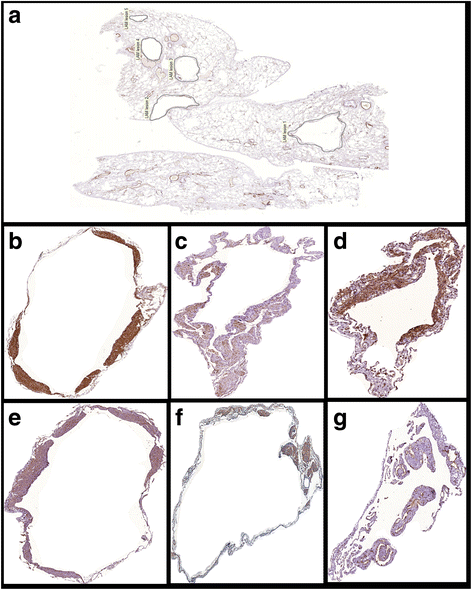
Methods: We analyzed morphological and functional parameters of thirty-three patients. Two groups of disease severity were identified according to FEV1 values. Lung tissue from open biopsies or lung transplants was immunostained for SMA, HMB-45, mTOR, VEGF-D, MMP-9 and D2-40. Density of cysts, density of nodules and protein expression were measured by image analysis and correlated with PFT parameters.
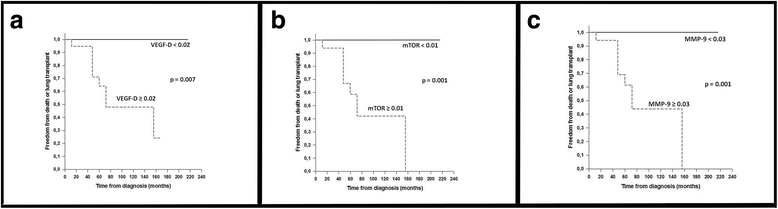
Results: There was no difference in the expression of D2-40 between the more severe and the less severe groups. All other immunohistological parameters showed significantly higher values in the more severe group (p ≤ 0.002). The expression of VEGF-D, MMP-9 and mTOR in LAM cells was associated with the density of both cysts and nodules. The density of cysts and nodules as well as the expression of MMP-9 and VEGF-D were associated with the impairment of PFT parameters.
Conclusions: Severe LAM represents an active phase of the disease with high expression of VEGF-D, mTOR, and MMP-9, as well as LAM cell infiltration. Our findings suggest that the tissue expression levels of VEGF-D and MMP-9 are important parameters associated with the loss of pulmonary function and could be considered as potential severity markers in open lung biopsies of LAM patients.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; Metalloproteinase; Pulmonary function tests; VEGF-D; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the review board for the human ethics committee of Sao Paulo University (CAPPesq-FMUSP n° 0623/09). The study is retrospective and used medical records and archived material from the Department of Pathology of Sao Paulo University Medical School.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A, Nicholson AG. WHO classification of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. 4. Lyon, FR: IARC; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Baldi BG, Freitas CS, Araujo MS, et al. Clinical course and characterization of lymphangioleiomyomatosis in a brazilian reference centre. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2014;31(2):129–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

