NADH/NADPH bi-cofactor-utilizing and thermoactive ketol-acid reductoisomerase from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
- PMID: 29739976
- PMCID: PMC5940873
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25361-4
NADH/NADPH bi-cofactor-utilizing and thermoactive ketol-acid reductoisomerase from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
Abstract
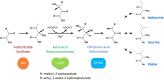
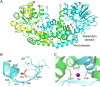
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) is a bifunctional enzyme in the second step of branched-chain amino acids biosynthetic pathway. Most KARIs prefer NADPH as a cofactor. However, KARI with a preference for NADH is desirable in industrial applications including anaerobic fermentation for the production of branched-chain amino acids or biofuels. Here, we characterize a thermoacidophilic archaeal Sac-KARI from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius and present its crystal structure at a 1.75-Å resolution. By comparison with other holo-KARI structures, one sulphate ion is observed in each binding site for the 2'-phosphate of NADPH, implicating its NADPH preference. Sac-KARI has very high affinity for NADPH and NADH, with K M values of 0.4 μM for NADPH and 6.0 μM for NADH, suggesting that both are good cofactors at low concentrations although NADPH is favoured over NADH. Furthermore, Sac-KARI can catalyze 2(S)-acetolactate (2S-AL) with either cofactor from 25 to 60 °C, but the enzyme has higher activity by using NADPH. In addition, the catalytic activity of Sac-KARI increases significantly with elevated temperatures and reaches an optimum at 60 °C. Bi-cofactor utilization and the thermoactivity of Sac-KARI make it a potential candidate for use in metabolic engineering or industrial applications under anaerobic or harsh conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong FB, Hedgecock CJR, Reary JB, Whitehouse D, Crout DHG. Stereochemistry of the reductoisomerase and αβ-dihydroxyacid dehydratase-catalysed steps in valine and isoleucine biosynthesis. Observation of a novel tertiary ketol rearrangement. J Chem Soc Chem Commun. 1974;9:351–352. doi: 10.1039/C39740000351. - DOI
-
- Armstrong FB, Lipscomb EL, Crout DHG, Mitchell MB, Prakash SR. Biosynthesis of valine and isoleucine: synthesis and biological activity of (2S)-α-acetolactic acid (2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoic acid), and (2R)- and (2S)-α-acetohydroxybutyric acid (2-ethyl-2-hydroxy-3-oxobutanoic acid) J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1983;1:1197–1201. doi: 10.1039/P19830001197. - DOI
-
- Hill RK, Sawada S, Arfin SM. Stereochemistry of valine and isoleucine biosynthesis: IV. Synthesis, configuration, and enzymatic specificity of α-acetolactate and α-aceto-α-hydroxybutyrate. Bioorg Chem. 1979;8:175–189. doi: 10.1016/0045-2068(79)90003-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

