Hyperactivity of Rac1-GTPase pathway impairs neuritogenesis of cortical neurons by altering actin dynamics
- PMID: 29740022
- PMCID: PMC5940682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25354-3
Hyperactivity of Rac1-GTPase pathway impairs neuritogenesis of cortical neurons by altering actin dynamics
Abstract
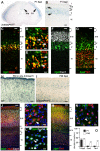
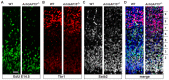
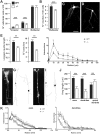
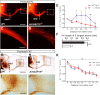
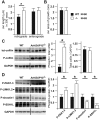
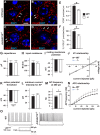
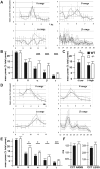
The small-GTPase Rac1 is a key molecular regulator linking extracellular signals to actin cytoskeleton dynamics. Loss-of-function mutations in RAC1 and other genes of the Rac signaling pathway have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Intellectual Disability (ID). The Rac1 activity is negatively controlled by GAP proteins, however the effect of Rac1 hyperactivity on neuronal networking in vivo has been poorly studied. ArhGAP15 is a Rac-specific negative regulator, expressed in the main subtypes of pyramidal cortical neurons. In the absence of ArhGAP15, cortical pyramidal neurons show defective neuritogenesis, delayed axonal elongation, reduced dendritic branching, both in vitro and in vivo. These phenotypes are associated with altered actin dynamics at the growth cone due to increased activity of the PAK-LIMK pathway and hyperphosphorylation of ADF/cofilin. These results can be explained by shootin1 hypo-phosphorylation and uncoupling with the adhesion system. Functionally, ArhGAP15-/- mice exhibit decreased synaptic density, altered electroencephalographic rhythms and cognitive deficits. These data suggest that both hypo- and hyperactivation of the Rac pathway due to mutations in Rac1 regulators can result in conditions of ID, and that a tight regulation of Rac1 activity is required to attain the full complexity of the cortical networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lelieveld, S. H. et al. Meta-analysis of 2,104 trios provides support for 10 new genes for intellectual disability. Nat. Neurosci. 10.1038/nn.4352 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

