The kinase domain of CK1 enzymes contains the localization cue essential for compartmentalized signaling at the spindle pole
- PMID: 29742018
- PMCID: PMC6080649
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0129
The kinase domain of CK1 enzymes contains the localization cue essential for compartmentalized signaling at the spindle pole
Abstract
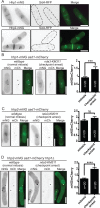
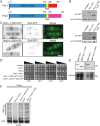
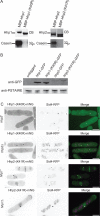
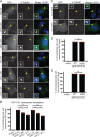
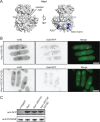
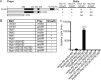
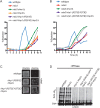
CK1 protein kinases contribute to multiple biological processes, but how they are tailored to function in compartmentalized signaling events is largely unknown. Hhp1 and Hhp2 (Hhp1/2) are the soluble CK1 family members in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. One of their functions is to inhibit the septation initiation network (SIN) during a mitotic checkpoint arrest. The SIN is assembled by Sid4 at spindle pole bodies (SPBs), and though Hhp1/2 colocalize there, it is not known how they are targeted there or whether their SPB localization is required for SIN inhibition. Here, we establish that Hhp1/2 localize throughout the cell cycle to SPBs, as well as to the nucleus, cell tips, and division site. We find that their catalytic domains but not their enzymatic function are used for SPB targeting and that this targeting strategy is conserved in human CK1δ/ε localization to centrosomes. Further, we pinpoint amino acids in the Hhp1 catalytic domain required for SPB interaction; mutation of these residues disrupts Hhp1 association with the core SPB protein Ppc89, and the inhibition of cytokinesis in the setting of spindle stress. Taken together, these data have enabled us to define a molecular mechanism used by CK1 enzymes to target a specific cellular locale for compartmentalized signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Agostinis P, Pinna LA, Meggio F, Marin O, Goris J, Vandenheede JR, Merlevede W. (1989). A synthetic peptide substrate specific for casein kinase I. FEBS Lett , 75–78. - PubMed
-
- Babu P, Bryan JD, Panek HR, Jordan SL, Forbrich BM, Kelley SC, Colvin RT, Robinson LC. (2002). Plasma membrane localization of the Yck2p yeast casein kinase 1 isoform requires the C-terminal extension and secretory pathway function. J Cell Sci , 4957–4968. - PubMed
-
- Babu P, Deschenes RJ, Robinson LC. (2004). Akr1p-dependent palmitoylation of Yck2p yeast casein kinase 1 is necessary and sufficient for plasma membrane targeting. J Biol Chem , 27138–27147. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A, 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR. (1998). Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast , 943–951. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya RP, Remenyi A, Good MC, Bashor CJ, Falick AM, Lim WA. (2006). The Ste5 scaffold allosterically modulates signaling output of the yeast mating pathway. Science , 822–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

