Characteristics and management of pyogenic liver abscess: A European experience
- PMID: 29742700
- PMCID: PMC5959441
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010628
Characteristics and management of pyogenic liver abscess: A European experience
Abstract
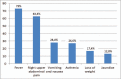
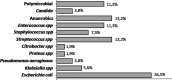
Pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) are space-occupying lesions in the liver associated with high morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study is to review an Italian hospital experience in epidemiological, clinical patterns, and management of PLA.We performed a retrospective, descriptive case series at a single center assessing demographic characteristics, presentation patterns, etiological factors, microbiological etiology, and management for patients treated for PLA between 2000 and 2016.Around 109 patients were identified. The majority of patients presented with fever (73%); right upper abdominal pain in 63.3%, vomiting and nausea in 28.4%. The most common laboratory abnormality among included items was increased C-reactive protein and fibrinogen blood levels, respectively, in 98% and 93.9% of cases. Abdominal ultrasound was the diagnostic investigation in 42.4% of cases; CT scan and MR imaging were performed in 51.1% and 3.3% of cases respectively. We observed blood or pus culture study in 99 cases of which only 53.5% came with positive microbial reports. The most common organism identified was Escherichia coli (26.5%), followed by Streptococcus spp (13.2%). Early antibiotic treatment started on all patients and 66.7% of cases required different approaches, Ultrasound or CT-guided needle aspiration of PLA was performed in 13 patients (11%) and percutaneous abscess drainage was performed on 72 patients (67%).PLA is a diagnostically challenging problem due to nonspecific presenting characteristics. The microbiological yield identified was a typical European spectrum with a preponderance of Escherichia coli infections. Once recognized, percutaneous drainage and antibiotic treatment are the mainstay of management for PLA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:1654–9. - PubMed
-
- Kuo SH, Lee YT, Li CR, et al. Mortality in emergency department sepsis score as a prognostic indicator in patients with pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Emerg Med 2013;31:916–21. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez Pérez JA, Gonzàlez JJ, Baldonedo RF, et al. Clinical course, treatment and multivariate analysis of risk factors for pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Surg 2001;181:177–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous