Arterial spin labeling MR imaging aids to identify cortical venous drainage of dural arteriovenous fistulas
- PMID: 29742722
- PMCID: PMC5959413
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010697
Arterial spin labeling MR imaging aids to identify cortical venous drainage of dural arteriovenous fistulas
Abstract
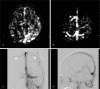
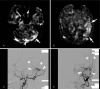
Cortical venous drainage (CVD) increases the probability of intracranial hemorrhage and mortality rate of dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF). Although digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the most accurate method to determine CVD in DAVFs, this modality has limitations due to its invasive nature and radiation issues. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic utility of arterial spin-labeling perfusion-weighted images (ASL-PWI) to identify CVD in patients with DAVF.The Institutional Review Board of our hospital approved this retrospective study. ASL-PWI features of 22 patients with DAVF were retrospectively reviewed for the presence of bright signal intensity in cortical veins and brain parenchyma. DAVF with bright signal intensity in cortical veins and/or brain parenchyma was regarded as having CVD. Using DSA as a reference standard, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of ASL-PWI for detecting CVD were calculated.Based on DSA features, 11 (11/22, 50%) patients were classified as having "aggressive" pattern with CVD. Eleven (11/22, 50%) patients also showed bright signal intensity in cortical veins (9/22, 41%) and/or brain parenchyma (4/22, 18%) on ASL-PWI. The 11 patients who had "Aggressive" pattern on DSA were the same 11 patients who were classified as having "aggressive" pattern on ASL-PWI. ASL-PWI showed perfect diagnostic performance for identifying CVD with sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of 100% for all.Thus, ASL-PWI could be used as a noninvasive mean to predict the presence of CVD in patients with DAVFs. It has the potential as a screening tool to evaluate DAVF prior to invasive DSA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Cortical Venous Drainage and Determination of the Borden Type of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Means of 3D Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin-Labeling MRI.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Jul;207(1):163-9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15171. Epub 2016 Apr 15. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016. PMID: 27082987
-
Association of developmental venous anomalies with perfusion abnormalities on arterial spin labeling and bolus perfusion-weighted imaging.J Neuroimaging. 2015 Mar-Apr;25(2):243-250. doi: 10.1111/jon.12119. Epub 2014 Apr 9. J Neuroimaging. 2015. PMID: 24717021
-
Jugular venous reflux may mimic type I dural arterio-venous fistula on arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance images.Neuroradiology. 2020 Apr;62(4):447-454. doi: 10.1007/s00234-019-02346-2. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Neuroradiology. 2020. PMID: 31898766
-
Diagnostic accuracy of arterial spin labeling MR imaging in detecting cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Aug 27;47(1):492. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02659-8. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39190141
-
[Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. Experience after 81 cases and literature review].Neurocirugia (Astur). 2013 Jul-Aug;24(4):141-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neucir.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2013. PMID: 23582488 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Retrograde Flow Into the Internal Jugular Vein in a Hemodialysis Patient Mimicking Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jan 28;16(1):e53092. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53092. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38414703 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical applications of arterial spin labeling of the intracranial compartment in vascular anomalies-A case-based review.Neuroradiol J. 2023 Dec;36(6):638-650. doi: 10.1177/19714009221130490. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Neuroradiol J. 2023. PMID: 36172883 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial Spin Labeling Was Useful for Evaluating the Treatment Response of a Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021;15(2):113-119. doi: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2019-0119. Epub 2020 Sep 17. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021. PMID: 37502803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Dijk JMC, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC. Clinical course of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke 2002;33:1233–6. - PubMed
-
- Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 1995;194:671–80. - PubMed
-
- Brown RD, Flemming KD, Meyer FB, et al. Natural history, evaluation, and management of intracranial vascular malformations. Mayo Clinic Proc 2005;80:269–81. - PubMed
-
- Detre JA, Leigh JS, Williams DS, et al. Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 1992;23:37–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

