Ablation of proliferating neural stem cells during early life is sufficient to reduce adult hippocampal neurogenesis
- PMID: 29742815
- PMCID: PMC6167166
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.22962
Ablation of proliferating neural stem cells during early life is sufficient to reduce adult hippocampal neurogenesis
Abstract
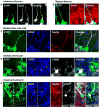
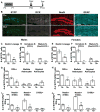
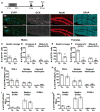
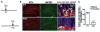
Environmental exposures during early life, but not during adolescence or adulthood, lead to persistent reductions in neurogenesis in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). The mechanisms by which early life exposures lead to long-term deficits in neurogenesis remain unclear. Here, we investigated whether targeted ablation of dividing neural stem cells during early life is sufficient to produce long-term decreases in DG neurogenesis. Having previously found that the stem cell lineage is resistant to long-term effects of transient ablation of dividing stem cells during adolescence or adulthood (Kirshenbaum, Lieberman, Briner, Leonardo, & Dranovsky, ), we used a similar pharmacogenetic approach to target dividing neural stem cells for elimination during early life periods sensitive to environmental insults. We then assessed the Nestin stem cell lineage in adulthood. We found that the adult neural stem cell reservoir was depleted following ablation during the first postnatal week, when stem cells were highly proliferative, but not during the third postnatal week, when stem cells were more quiescent. Remarkably, ablating proliferating stem cells during either the first or third postnatal week led to reduced adult neurogenesis out of proportion to the changes in the stem cell pool, indicating a disruption of the stem cell function or niche following stem cell ablation in early life. These results highlight the first three postnatal weeks as a series of sensitive periods during which elimination of dividing stem cells leads to lasting alterations in adult DG neurogenesis and stem cell function. These findings contribute to our understanding of the relationship between DG development and adult neurogenesis, as well as suggest a possible mechanism by which early life experiences may lead to lasting deficits in adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
Keywords: GFAP-Tk; adult neurogenesis; dentate gyrus; early postnatal neurogenesis; hippocampal stem cells.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Aisa B, Elizalde N, Tordera R, Lasheras B, Del Rio J, Ramirez MJ. Effects of neonatal stress on markers of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: implications for spatial memory. Hippocampus. 2009;19(12):1222–31. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol. 1990;301(3):365–81. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41(5):683–6. - PubMed
-
- Angevine JB., Jr Time of neuron origin in the hippocampal region. An autoradiographic study in the mouse. Exp Neurol Suppl. 1965;(Suppl 2):1–70. - PubMed
-
- Baek SB, Bahn G, Moon SJ, Lee J, Kim KH, Ko IG, Kim SE, Sung YH, Kim BK, Kim TS, et al. The phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor, tadalafil, improves depressive symptoms, ameliorates memory impairment, as well as suppresses apoptosis and enhances cell proliferation in the hippocampus of maternal-separated rat pups. Neurosci Lett. 2011;488(1):26–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

