Cost-effectiveness of lung volume reduction coil treatment in patients with severe emphysema: results from the 2-year follow-up crossover REVOLENS study (REVOLENS-2 study)
- PMID: 29743071
- PMCID: PMC5941693
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-018-0796-x
Cost-effectiveness of lung volume reduction coil treatment in patients with severe emphysema: results from the 2-year follow-up crossover REVOLENS study (REVOLENS-2 study)
Abstract
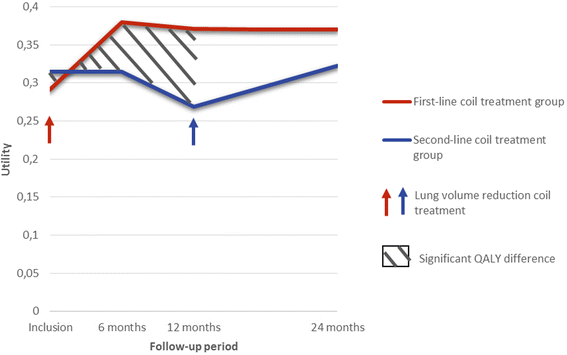
Background: The REVOLENS study compared lung volume reduction coil treatment to usual care in patients with severe emphysema at 1 year, resulting in improved quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) and higher costs. Durability of the coil treatment benefit and its cost-effectiveness at 2 years are now assessed.
Methods: After one year, the REVOLENS trial's usual care group patients received coil treatment (second-line coil treatment group). Costs and QALYs were assessed in both arms at 2 years and an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio in cost per QALY gained was calculated. The uncertainty of the results was estimated by probabilistic bootstrapping.
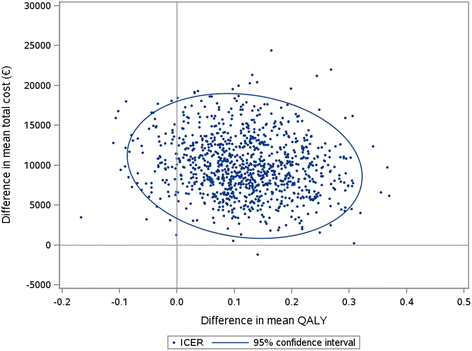
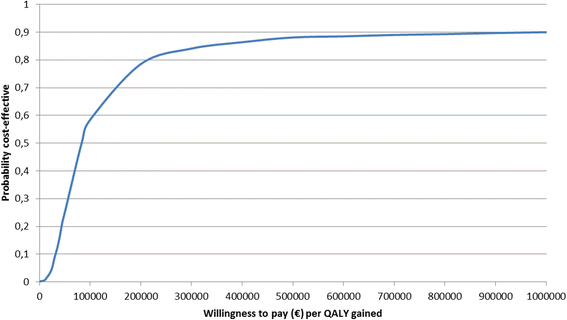
Results: The average cost of coil treatment in both groups was estimated at €24,356. The average total cost at 2 years was €9655 higher in the first-line coil treatment group (p = 0.07) and the difference in QALY between the two groups was 0.127 (p = 0.12) in favor of first-line coil treatment group. The 2-year incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) was €75,978 / QALY. The scatter plot of the probabilistic bootstrapping had 92% of the replications in the top right-hand quadrant.
Conclusion: First-line coil treatment was more expensive but also more effective than second-line coil treatment at 2 years, with a 2-year ICER of €75,978 / QALY.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01822795 .
Keywords: Coil treatment; Cost-effectiveness; QALY; Severe emphysema.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Ethics Committee of Dijon Est I and the French Agency for Medicines and Health Products Health approved the study protocol.
Competing interests
Hervé Mal received honorarium from Boehringer, Bayer, Roche, Astellas, Chiesi, Actellion, Pfizer, Novartis, GSK outside the submitted work; Charles Hugo Marquette has been involved as investigators in previous studies sponsored by BTG/PneumRx, and received travel reimbursements and speaker fees for educational sessions and consulting from BTG/PneumRx; Hervé Dutau received travel reimbursements and speaker fees for educational sessions and consulting from BTG/PneumRx; Arnaud Bourdin received honorarium from Astra Zeneca, GSK, Boehringer, Novartis, Teva, Chiesi, Actellion, Gilead, Roche outside the submitted work; Jean Michel Vergnon received travel reimbursements and speaker fees for educational sessions from BTG/PneumRx; Christophe Pison received honorarium from BTG/PneumRx and his hospital funds to conduct trials from Nuvaira, PulmonX, BTG/PneumRx; Vincent Jounieaux received travel reimbursements and speaker fees for educational sessions and consulting from BTG/PneumRx; Armelle Marceau received honorarium from BTG/PneumRx; Gaëtan Deslée has been involved as investigator in previous studies sponsored by BTG/PneumRx, and received travel reimbursements and speaker fees for educational sessions and consulting from BTG/PneumRx; Sylvie Leroy, Jeanne Marie Perotin, Romain Kessler, Mathieu Salaün, Margaux Bonnaire, Sylvain Dukic, Coralie Barbe, Isabelle Durand-Zaleski indicated no conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Makris D, Leroy S, Pradelli J, Benzaquen J, Guenard H, Perotin J-M, Zakynthinos S, Zakynthinos E, Deslee G, Marquette CH. Changes in dynamic lung mechanics after lung volume reduction coil treatment of severe emphysema. Thorax 2017. 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-210118. - PubMed
-
- Shah PL, Zoumot Z, Singh S, Bicknell SR, Ross ET, Quiring J, Hopkinson NS, Kemp SV, RESET trial Study group. Endobronchial coils for the treatment of severe emphysema with hyperinflation (RESET): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2013; 1: 233–240. - PubMed
-
- Deslée G, Mal H, Dutau H, Bourdin A, Vergnon JM, Pison C, Kessler R, Jounieaux V, Thiberville L, Leroy S, Marceau A, Laroumagne S, Mallet JP, Dukic S, Barbe C, Bulsei J, Jolly D, Durand-Zaleski I, Marquette CH, REVOLENS Study Group Lung volume reduction coil treatment vs usual Care in Patients with Severe Emphysema: the REVOLENS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:175–184. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.17821. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sciurba FC, Criner GJ, Strange C, Shah PL, Michaud G, Connolly TA, Deslée G, Tillis WP, Delage A, Marquette C-H, Krishna G, Kalhan R, Ferguson JS, Jantz M, Maldonado F, McKenna R, Majid A, Rai N, Gay S, Dransfield MT, Angel L, Maxfield R, Herth FJF, Wahidi MM, Mehta A, Slebos D-J, RENEW Study Research Group Effect of endobronchial coils vs usual care on exercise tolerance in patients with severe emphysema: the RENEW randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:2178–2189. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.6261. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

